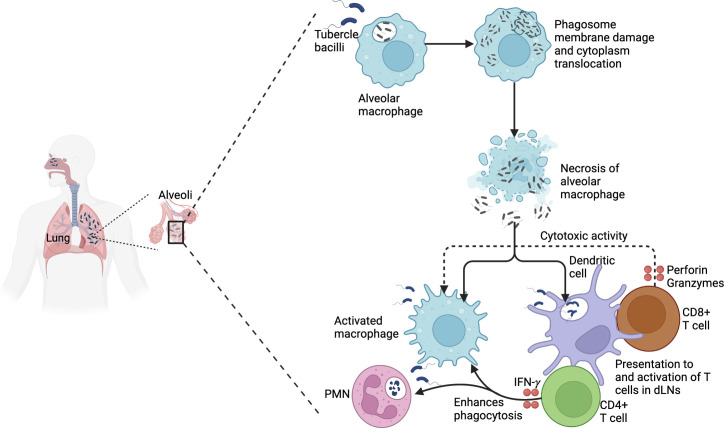
Figure 2.
TB pathogenesis. Virulent Mtb that is phagocytosed by alveolar macrophages causes phagosome membrane damage and translocates to the cytoplasm. This results in necrosis and spread to other macrophages and dendritic cells. Mtb is processed and presented to CD4+ T cells that produce IFN-γ, enhancing the phagocytosis of infected macrophages and polymorphonuclear cells. In addition, activated CD8+ T cells produce perforin and granzymes that mediate the cytotoxic activity of infected macrophages.