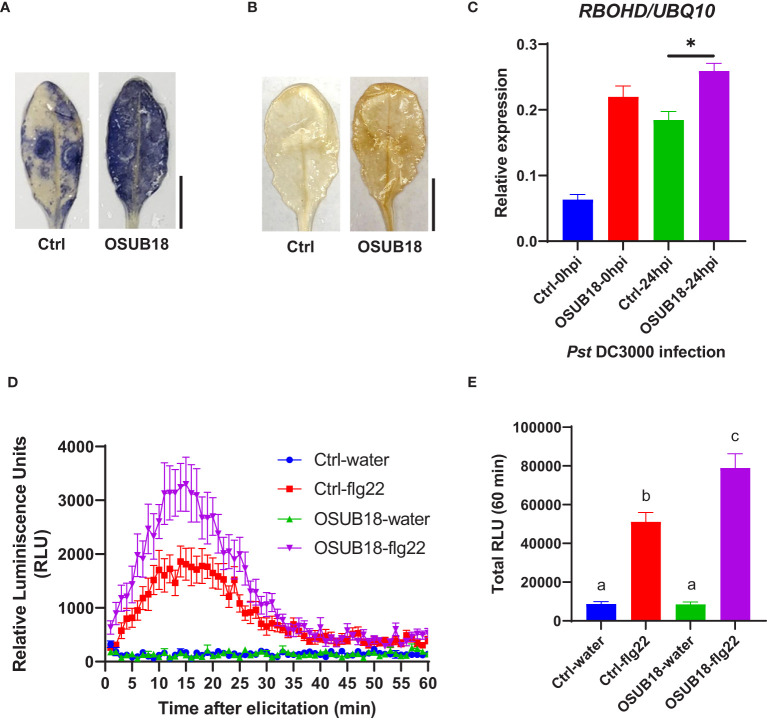
Figure 6.
OSUB18 root drench treatment triggered strong ISR in A thaliana against the bacterial pathogen Pst DC3000 via significantly stronger ROS production and higher RBOHD gene expression. (A) Col-0 plants drenched with OSUB18 produced more intense superoxide anion upon the Pst DC3000 infection (24hpi), as illustrated by the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) staining assay. Scale bar = 10 mm. (B) Col-0 plants drenched with OSUB18 produced more intense hydrogen peroxide upon the Pst DC3000 infection (24hpi), as illustrated by the 3,3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining assay. Scale bar = 10 mm. (C) Relative gene expression of the ROS-responsive gene RBOHD. Water or OSUB18-drenched plants were infected with Pst DC3000 by syringe injection. 0 or 24 hours later, the injected leaves were collected for the qRT-PCR assay. The UBQ10 gene was used as an internal reference in the qRT-PCR assay. (D) Col-0 plants pre-drenched with OSUB18 showed a more vigorous ROS burst elicited by the bacterial PAMP flg22. (E) Quantification of the ROS burst in (D). Data present mean ± SE of three biological replicates. Data with different letters or * indicate a p-value < 0.05 on Student’s t-test or ANOVA.