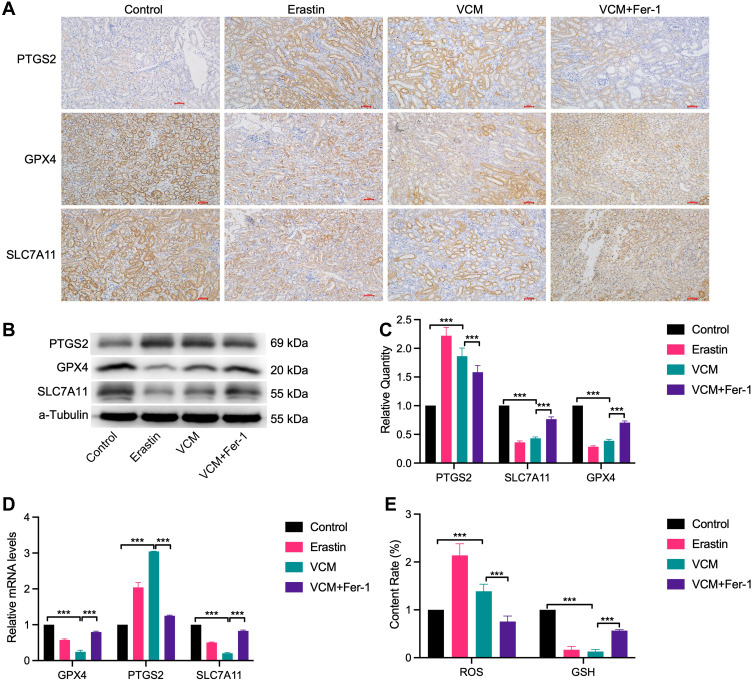
Figure 2.
VCM caused renal injury via inducing ferroptosis cell death in animals. (A) IHC staining showed that GPX4 and SLC7A11 were downregulated and PTGS2 was upregulated in the kidney tissues of VCM-treated mice. In addition, Fer-1 restored the expressions of GPX4 and SLC7A11 and reduced the expression of PTGS2 in mice injected with VCM. Expression levels of PTGS2, GPX4 and SLC7A11 in the kidney tissues of mice measured by (B) Western blotting analysis and (C) quantification of Western blotting results, (D) qRT-PCR analysis. The results indicated that VCM increased the expression of PTGS2 and decreased the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 at the mRNA and protein levels in the kidney tissues of mice. In addition, Fer-1 treatment restored the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 and decreased the expression of PTGS2 at the mRNA and protein levels in the kidney tissues of VCM-treated mice. (E) ELISA results revealed the accumulation of ROS and the reduction of GSH content in the serum of VCM-treated mice. Fer-1 treatment reversed the effects of VCM on serum ROS and GSH contents. ***P<0.001.