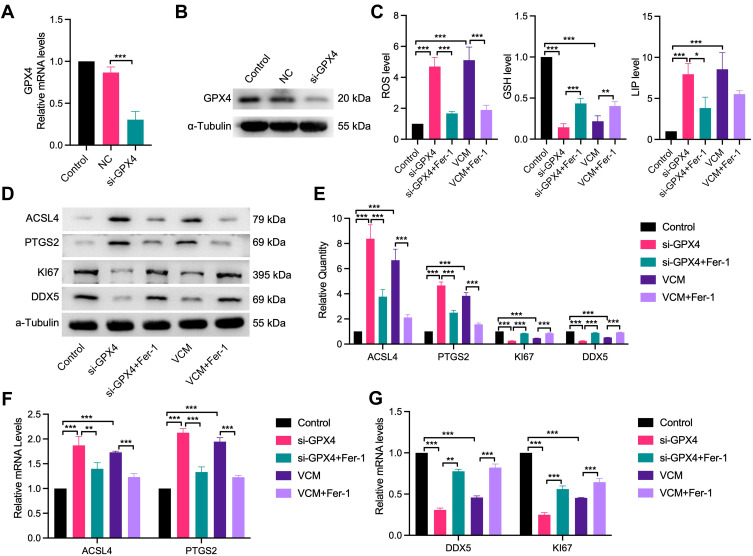
Figure 6.
VCM induced ferroptosis in HK-2 cells through downregulation of GPX4. HK-2 cells were transfected with siRNA NC or GPX4 siRNA (si-GPX4) for 24 h. (A) qRT-PCR and (B) Western blotting results confirming the knockdown efficiency of the GPX4-specific siRNA. (C) ELISA results revealing the contents of ROS, GSH and LIP in HK-2 cells. We observed that the contents of ROS and LIP increased, while that of GSH decreased in GPX4-KD HK-2 cells. Furthermore, Fer-1 co-treatment inhibited the accumulation of LIP and ROS and restored the content of GSH partly in GPX4-KD HK-2 cells. Expression levels of ACSL4, PTGS2, Ki67 and DDX5 in HK-2 cells measured by (D) Western blotting analysis, (E) quantification of Western blotting results and (F) qRT-PCR analysis. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of DDX5 and Ki67 at the mRNA level. The results revealed that GPX4 knockdown in HK-2 cells increased the expression of ACSL4 and PTGS2 and decreased the expression of DDX5 and Ki67 at the mRNA and protein levels. In addition, Fer-1 decreased the expression of ACSL4 and PTGS2 and restored the expression of DDX5 and Ki67 at the mRNA and protein levels in GPX4-KD HK-2 cells. These results were consistent with those observed in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.