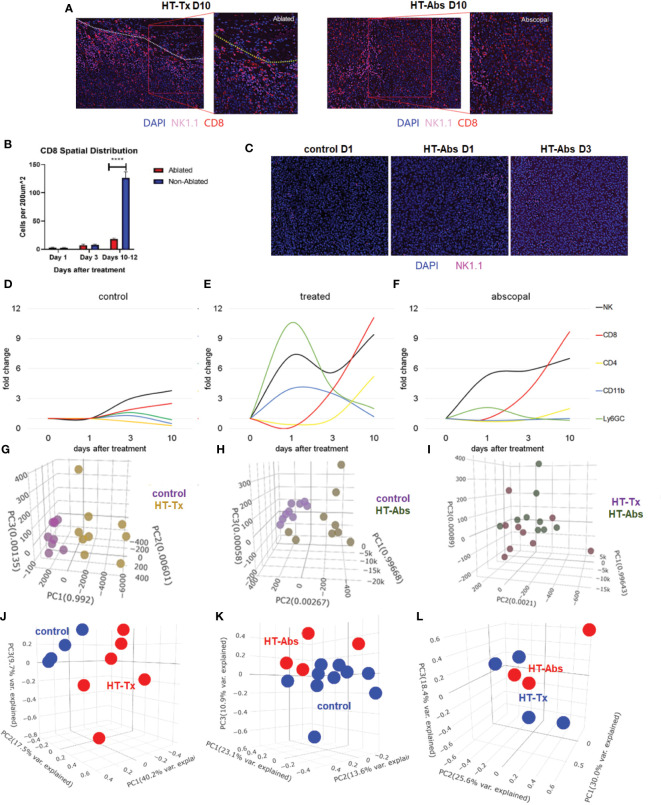
Figure 4.
The temporal kinetics of intratumoral cell infiltration are dissimilar at early time points and similar at later time points between histotripsy-treated and histotripsy-abscopal tumors. Mice bearing bilateral B16F10 tumors were treated with unilateral sham (control) or partial histotripsy ablation on day 10. (A) Multicolor immunofluorescence 10 days after unilateral B16F10 histotripsy ablation showed an influx of NK1.1+ and CD8+ cell populations within the non-ablated zones of histotripsy-treated (“HT-Tx”) tumors and diffusely in histotripsy-abscopal (“HT-Abs”) tumors. (B) Quantitation of CD8+ staining at various time points revealed delayed infiltration that was strictly localized to non-ablated zones (blue) and not ablated zones (red). (C) Multicolor immunofluorescence at early time points revealed infiltration of NK1.1+ cells in histotripsy-abscopal (“HT-Abs”) tumors. (D-F) Multicolor immunohistochemistry performed 1, 3 and 10 days after partial histotripsy ablation revealed minimal increases in NK1.1+ and CD8+ cells in control tumors over time (D). In contrast, histotripsy-treated tumors exhibited rapid influx of CD11b+ and Ly6GC+ and NK1.1+ cell populations immediately after ablation; whereas CD11b+ and Ly6CG+ cell infiltration was short-lived, NK1.1+ cell populations followed a biphasic pattern of early and delayed intratumoral infiltration; CD8+ and CD4+ cell infiltration followed a delayed pattern of delayed intratumoral infiltration (E). Whereas histotripsy-abscopal tumors did not exhibit the early pattern of CD11b+ and Ly6GC+ cell infiltration seen in histotripsy-treated tumors, patterns of NK1.1+ and CD8+ and CD4+ cell populations were similar to those observed in histotripsy-treated tumors (F). (G-I) Digital spatial profiling of immune-relevant protein expression within regions of lymphocytic infiltration was performed on control, histotripsy-treated (“HT-Tx”) and histotripsy-abscopal (“HT-Abs”) B16F10 tumors 10 days after unilateral sham or histotripsy ablation. Principal component analyses demonstrated differences in overall expression of immune-relevant proteins between control (purple) and histotripsy-treated (gold) tumors (G), and between control (purple) and histotripsy-abscopal (bronze) tumors (H); however, patterns of immune-relevant protein expression were largely superimposable between histotripsy-treated (brown) and histotripsy-abscopal (green) tumors (I). (J-L) RNASeq analyses of intratumoral CD45+ cells were performed on control, histotripsy-treated (“HT-Tx”) and histotripsy-abscopal (“HT-Abs”) B16F10 tumors 10 days after unilateral sham or histotripsy ablation. Principal component analyses demonstrated differences in overall transcriptional activity between control (blue) and histotripsy-treated (red) tumors (J) and between control (red) and histotripsy-abscopal tumors (blue) (K), but not between histotripsy-treated (blue) tumors and histotripsy-abscopal (red) tumors (L). (n=3-10 mice per experimental group; ****=p < 0.0001 between groups).