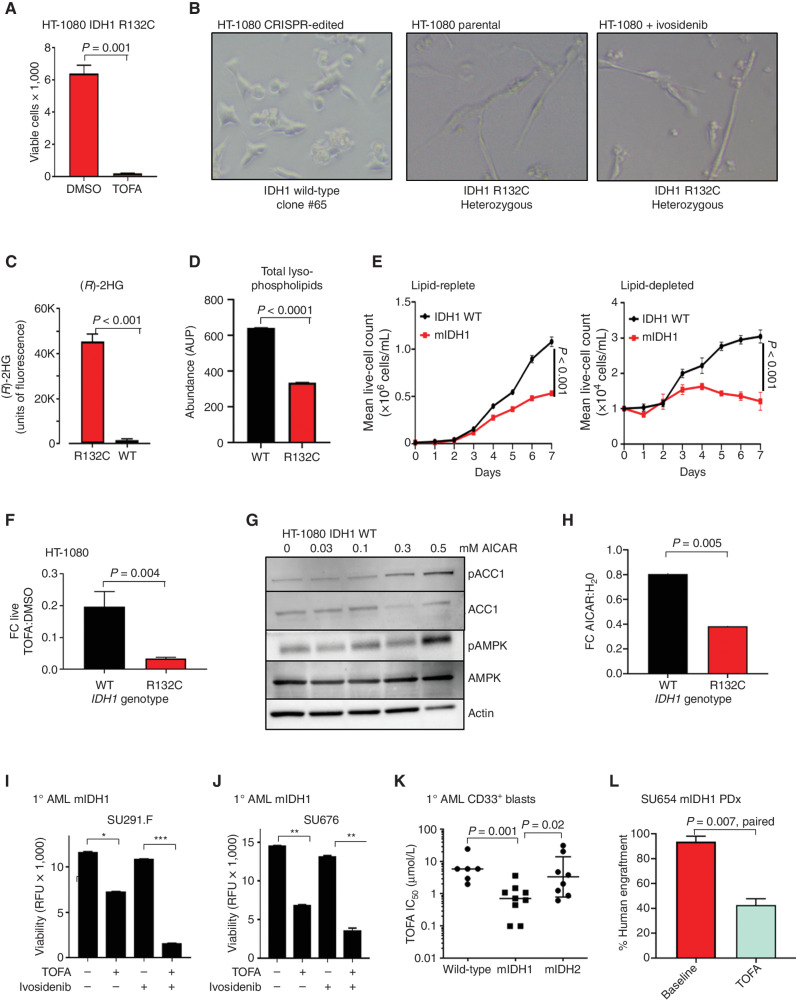
Figure 6.
ACC1 selective inhibitors have activity in mIDH1 cancers. A, Viability of HT-1080 mIDH1 R132C cells after exposure to 4 μmol/L TOFA for 72 hours measured by DAPI-negative cell population. B, Representative images of wild-type IDH1 reversion HT-1080 cells cultured at low density in 4% lipid-depleted serum or IDH1 R132C parental cells or IDH1 R132C treated with 10 μmol/L ivosidenib. Note that cells with IDH1 R132C mutation form ultrathin adherent elongated spindle-like cells. This morphology change was not reversed by coculture with ivosidenib. C, Measurement of 2HG in the supernatant of parental mIHD1 HT-1080 cells but undetectable in wild-type IDH1 reversion HT-1080 cells (clone #65 is shown as representative clone) after 72 hours. D, Total abundance of lysophospholipids (LPC + LPE) measured by LC-MS in mIDH1 vs. WT HT-1080 cultured in lipid-depleted media. AUP, area under the peak. E, Growth curves of mIDH1 vs. wild-type revertant HT-1080 in lipid-replete (left) vs. lipid-depleted (right) serum over 7 days. F, FC decrease in the number of live IDH1 R132C HT-1080 cells compared with IDH1 reversion wild-type HT-1080 cells after 96-hour exposure to the ACC1 inhibitor TOFA compared with DMSO vehicle. Graph shows mean of 3 independent experiments. G, Western blot showing increased phosphorylated ACC1 Serine 79 after treatment of HT-1080 wild-type cells with increasing concentration of AICAR. H, FC decrease in the number of live IDH1 R132C HT-1080 cells after 96-hour exposure to AICAR vs. H2O vehicle in comparison with IDH1 reversion wild-type HT-1080 cells under same conditions. Graph is a summary of 3 independent experiments. I and J, Primary mIDH1 AML cells isolated by flow cytometry from a patient at relapse (I) and a de novo patient (J) are sensitive to 10 μmol/L TOFA over 72 hours, but cytotoxicity is not reversed by 10 μmol/L ivosidenib. ***, P < 0.001;**, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05. RFU, relative fluorescence unit. K, Summary of TOFA IC50 at 72 hours after in vitro treatment of mIDH1, mIDH2, and IDH wild-type primary AML blasts cultured in low serum media. P value reflects nonparametric two-tailed comparison between groups; bars represent median IC50 in μmol/L. L, Engraftment of mIDH1 AML at baseline and after 30 days of treatment with either vehicle or 50 mg/kg TOFA given by daily intraperitoneal injection. P = 0.007, paired t test, treated vs. baseline. PDx, patient-derived xenograft; WT, wild-type.