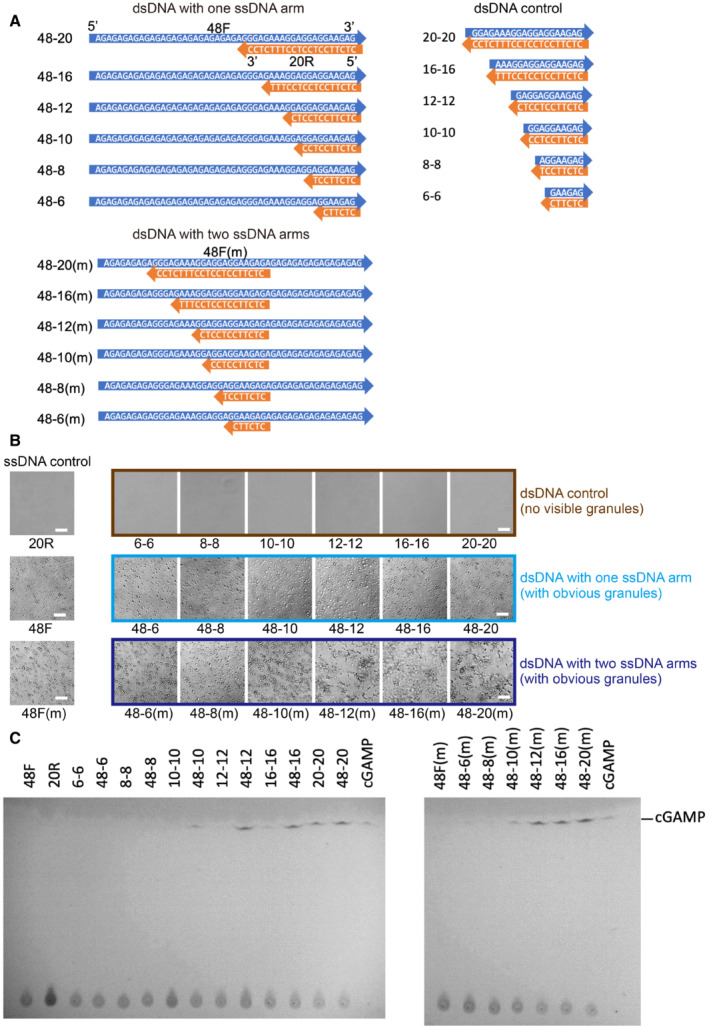
Photographs of FL‐hcGAS (0.294 mg/ml, 5.0 μM) mixed with indicated DNAs (2.5 μM) showing phase‐separated droplets or condensates induced by short dsDNAs with ssDNA arms but not the short dsDNA controls (n = 2, biological replicates, data from one representative independent biological replicate are shown). The corresponding concentration in mg/ml were 0.009 for 6–6, 0.012 for 8–8, 0.014 for 10–10, 0.018 for 12–12, 0.024 for 16–16, 0.031 for 20–20, 0.043 for 48–6 and 48‐6(m), 0.044 for 48–8 and 48‐8(m), 0.046 for 48–10 and 48–10(m), 0.047 for 48–12 and 48‐12(m), 0.05 for 48–16 and 48–16(m), 0.053 for 48–20 and 48–20(m), 0.015 for 20R, and 0.038 for 48F and 48F(m). The scale bar represents 20 μm.