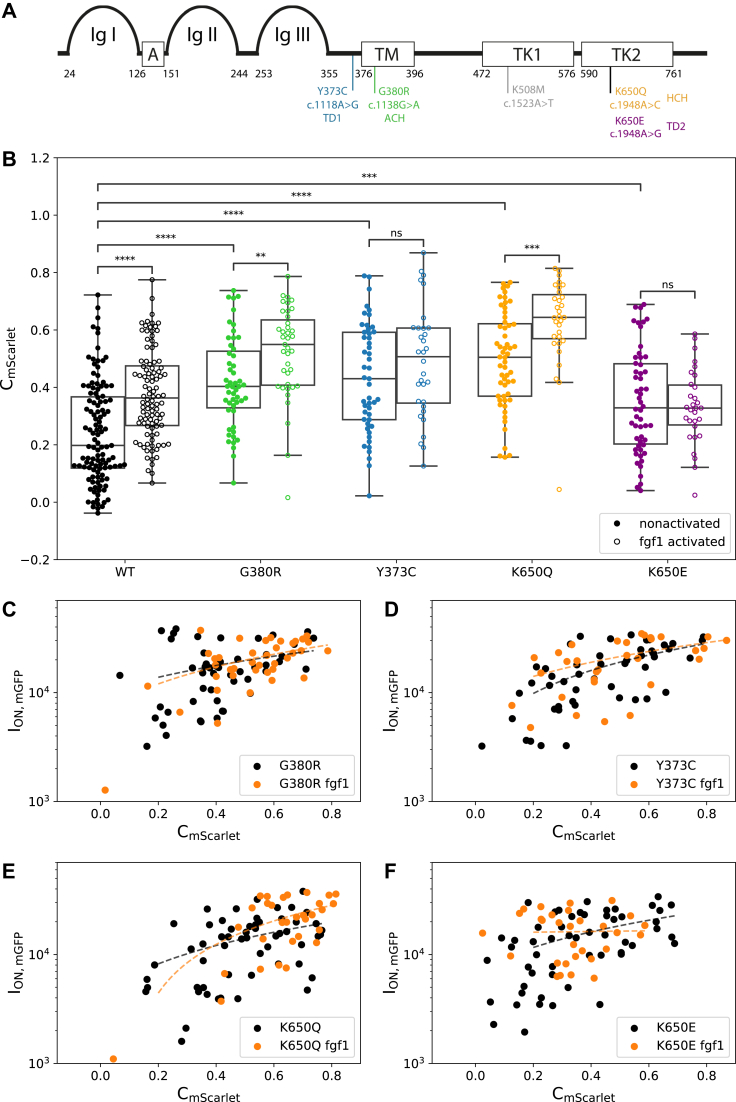
Figure 2.
Effect of FGFR3 mutations on receptor activation levels.A, schematic representation of the FGFR3 and the different tested mutations: Ig-like domains (Ig I–Ig III); acidic box (A), transmembrane (TM) domain, and an intracellular split tyrosine kinase domain (TK1 and TK2). Numbers indicate the amino acid position of the respective domains. Mutations are indicated at their approximate location in the protein domains with their respective amino acid and nucleotide substitutions and associated congenital disorder. B, comparison of the adaptor contrast (CmScarlet) determined for the WT and mutant forms of FGFR3 in the absence and presence of fgf1. C–F, correlation between the receptor intensity in ON areas (ION,mGFP) and the adaptor contrast (CmScarlet) for the mutant receptors (Spearman correlation coefficients [r] for each mutant are listed in Table S1). The p value annotation legend is ∗0.01 ≤ p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗0.001 ≤ p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗0.0001 ≤ p ≤ 0.001; and ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001. A full list of p values can be found in Table S3. FGFR3, fibroblast growth factor receptor 3; Ig, immunoglobulin.