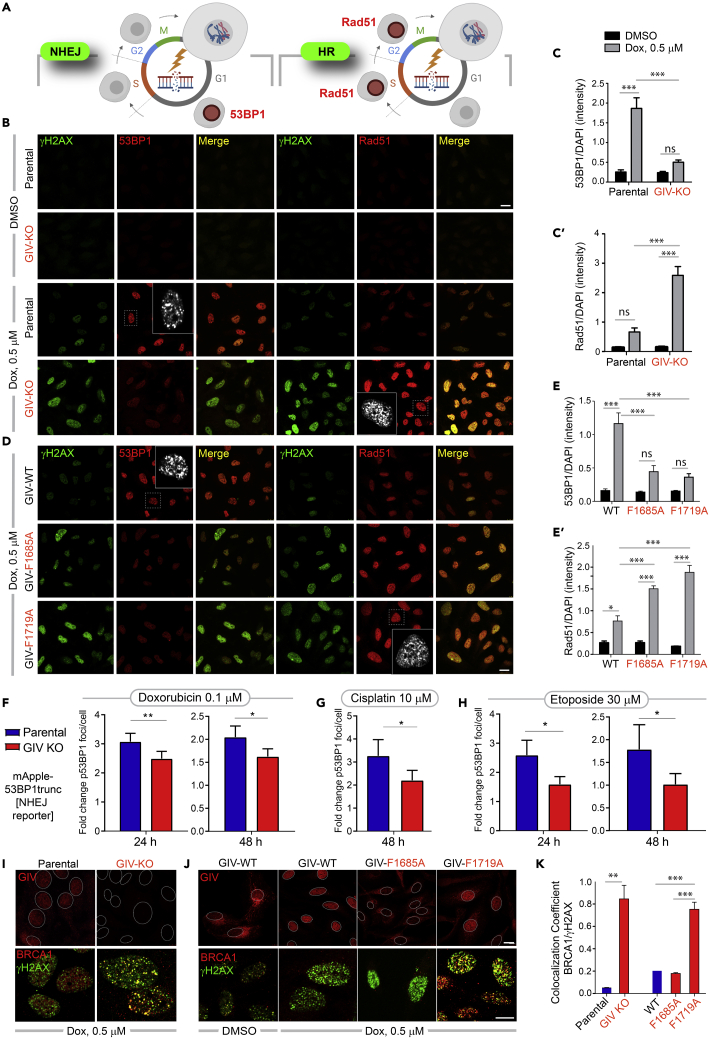
Figure 6.
GIV inhibits HR, favors NHEJ, and inhibits the localization of BRCA1 to sites of DNA damage
(A) Schematic summarizing the two markers, 53BP1 (left) and Rad51 (right) commonly used to monitor the repair pathway of choice (NHEJ vs. HR, respectively) after DNA damage.
(B–E′) Control (parental) and GIV-depleted (GIV KO) HeLa cells (B-C) or GIV-depleted HeLa cells stably expressing WT or mutant GIV constructs (D-E) were challenged with Dox or vehicle control (DMSO) prior to being fixed with Methanol and co-stained for γH2AX (green) and 53BP1 (red; left) or Rad51 (red; right) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Representative images are shown in B and D (scale bar = 15 μm). Insets show the magnified view of a single cell (interrupted box) in the field, highlighting the punctate nature of the nuclear staining for 53BP1 or Rad51. Bar graphs in C-C′ and E-E′ show the quantification of the intensity of 53BP1 or Rad51 staining normalized to DAPI. Data displayed as mean ± SEM and one-way ANOVA to determine significance. (∗; p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗; p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗; p ≤ 0.001; ns = not significant).
(F–H) Bar graphs display the fold change in the number of bright foci of 53BP1 in parental and GIV KO HeLa cells stably expressing mApple-53BP1 reporter (which detects NHEJ) upon challenge with the indicated concentrations of Doxorubicin (F), Cisplatin (G) or Etoposide (H). Data displayed as mean ± SEM and t-test to determine significance. (∗; p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗; p ≤ 0.01). See also Figures S7A and S7B for 53BP1 reporter studies on parental and GIV KO MDA-MB-231cells.
(I–K) HeLa cell lines in B, D were treated as in B, D, and fixed and analyzed for GIV (top) and BRCA1 (bottom) localization with respect to the nuclei (demarcated with interrupted oval outlines). Representative images are shown in I-J (scale bar = 15 μm). See Table S4 for predicted nuclear localization signals in GIV. See also Figures S7B and S7C for expanded individual panels. Bar graphs in K show Pearson’s colocalization coefficient for the degree of colocalization observed within the nucleus between BRCA1 (red) and γH2AX (green).