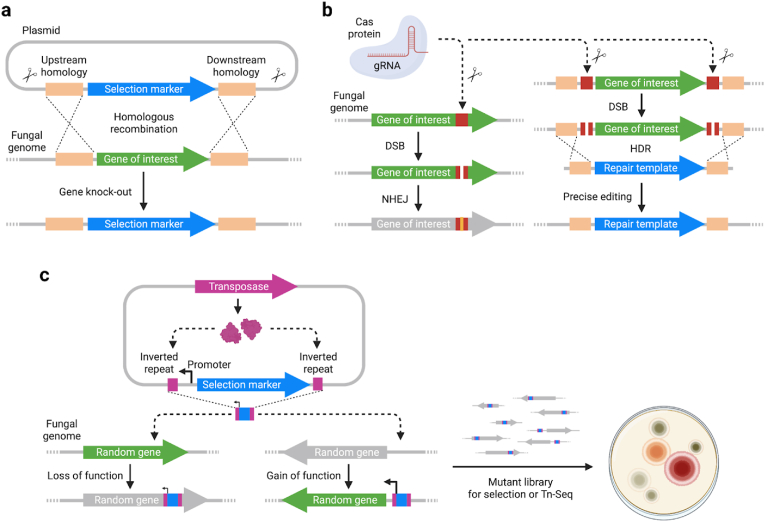
Fig. 4.
Tools for generating mutants and modifying the fungal genome. (a) Homology arms on the genetic payload and the host genome promote homologous recombination. Double crossover of DNA fragments result in swapping of the gene of interest with a selection marker, usually conferring resistance to antibiotics. (b) Cas protein targets a specific DNA sequence on the host genome with the help from guide RNA (gRNA) and generates double-strand break (DSB). DSB repaired by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) usually leads to loss of function of the gene. Alternatively, homology directed repair (HDR) uses a repair template, usually a provided linearized DNA, to precisely edit the host genome. (c) Transposon harboring an outward-facing promoter either inactivates a gene when inserted in its coding sequence or activates a previously inactive gene in the neighborhood of insertion, generating a diverse mutant library for downstream selection or Tn-Seq.