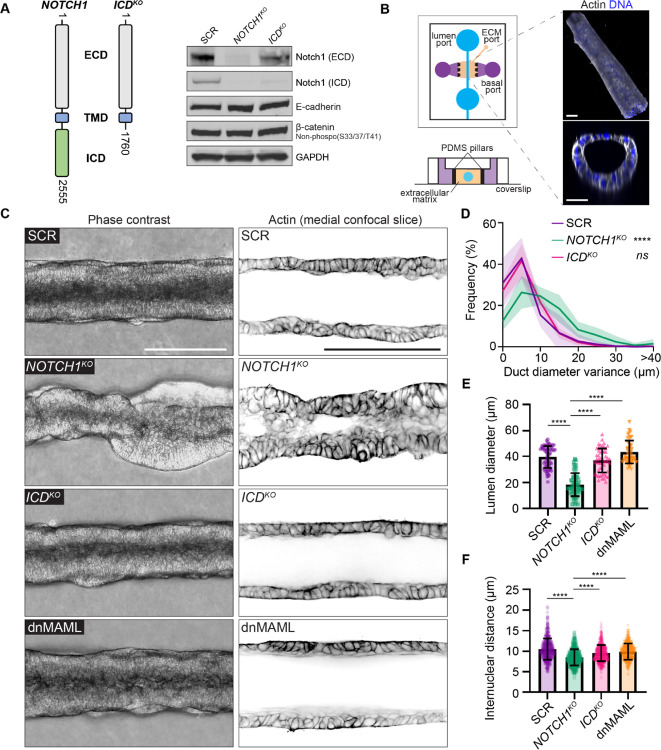
Figure 1. Notch1 influences ductal epithelium architecture through a transcription-independent mechanism.
(A) Left: Schematic of endogenous Notch1 CRISPR-Cas9 mutant used to truncate Notch1 ICD. Right: Western blot of lysates from scramble control (SCR), NOTCH1KO, and ICDKO monolayers immunoblotted for Notch1 ECD, Notch1 ICD, E-Cadherin, β-Catenin (non-phosphorylated (S33/37/T41)), and GAPDH. (B) Left: Organotypic microfluidic platform consisting of an engineered 3D mammary ductal epithelium embedded in physiologic ECM. Luminal ports (blue) used for cell seeding and perfusion of medium through the lumen, basal ports (purple) used for delivery of medium containing growth factors, ECM injection port and ECM compartment (beige), PDMS pillars (black) used to contain hydrogel ECM (Top schematic: top-down view; bottom schematic: cross-section). Right: Representative 3D oblique projection (top) and cross-section (bottom) of a 3D mammary duct labeled with phalloidin (grey) and Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 50 μm. (C) Left: Representative phase contrast micrographs of SCR, NOTCH1KO, ICDKO, and dnMAML ducts. Scale bar, 150 μm. Right: Representative medial confocal slice fluorescence micrographs of SCR, NOTCH1KO, ICDKO, and dnMAML epithelial ducts labeled with phalloidin (black). Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Quantification of duct diameter variance measured from phase contrast micrographs as shown in C. n = 8, 7, 7 ducts from three independent experiments. (E) Quantification of lumen diameter measured from confocal micrographs of phalloidin as shown in C. n ≥ 10 average lumen diameters, from three independent experiments. (F) Quantification of internuclear distances measured from confocal micrographs of Hoechst labeled ducts. n ≥ 40 internuclear distances per duct from three independent experiments. For all plots, mean ± SEM; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test, ****p<0.0001.