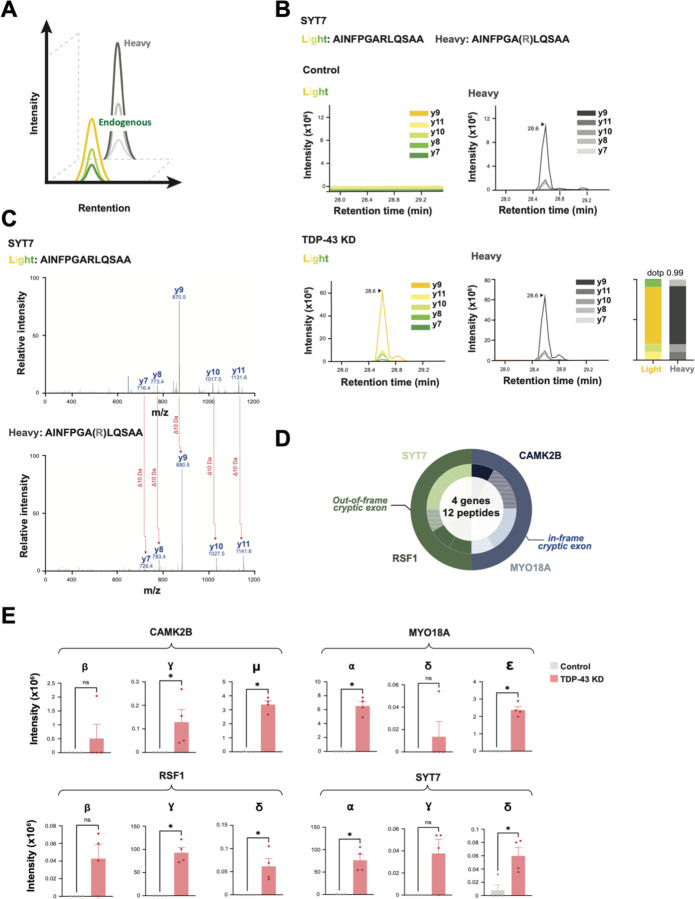
Fig. 5. Scalable cryptic peptide validation in TDP-43 deficient neurons by targeted proteomics.
(A) Schematic of parallel reaction monitoring targeted mass spectrometry (PRM-MS). Co-elution of stable heavy isotope- labeled peptides (SIL peptides) allows for ultra-sensitive measurement of corresponding endogenous peptides. (B) PRM-MS assay using a synthetic SIL peptide internal standard identifies a cryptic peptide in SYT7 in TDP-43 KD, but not control, iNeurons. Spectral plot of heavy standards and light (endogenous) y-ions from an SYT7 cryptic peptide are shown, with accompanying dot plots. (C) Corresponding mass spectra of endogenous and heavy peptide standards of the SYT7 cryptic peptide in TDP-43 depleted iPSC neurons. (D) Detection of 12 trypsin-digested cryptic peptides across 4 genes using single-shot PRM assays in TDP-43 KD iPSC neuron lysates. Outer circle represents the gene, and inner circle represents the number of cryptic peptides detected by PRM per gene. Hatched color signifies successful detection of 1–2 y-ions; solid color signifies detection of 3 or more y-ions. (E) Quantification of cryptic peptide expression in control and TDP-43 KD iPSC neurons using PRM assays. n= 4 replicates per sample. Two-sample t-test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.001