Figure 2.
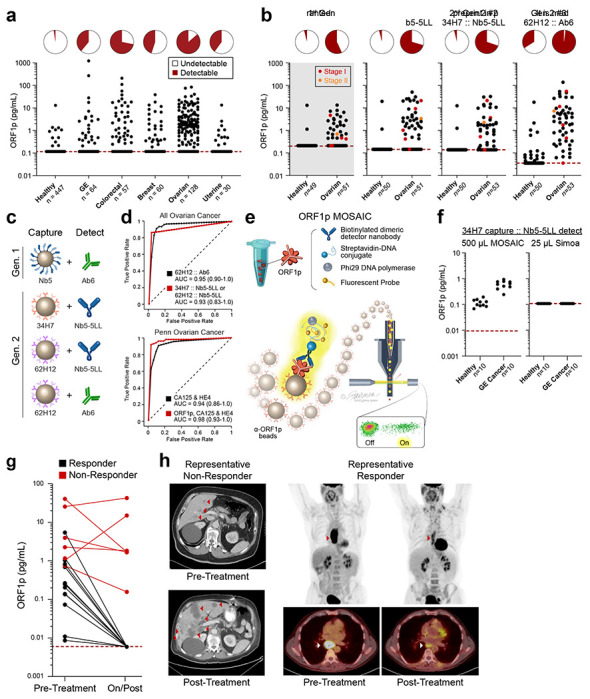
Improved detection of ORF1p with second-generation assays and potential clinical utility. a, 34H7::Nb5-5LL second-generation assay measurements across a multi-cancer cohort. b, Ovarian cancer patients with age- and gender-matched controls in first- and second-generation assays; patients are a subset of those in 2a; red dots: stage I disease, orange dots: stage II disease. c, Schematic of affinity reagents used. 34H7 and 62H2 are custom mAbs; Nb5-5LL is an engineered homodimeric nanobody. d, ROC curves with single marker ORF1p across all healthy and ovarian cancer patients (top, n=128-132 cancer, 447-455 healthy), and multivariate models for ovarian (bottom, n=51-53 cancer, 50 healthy). e, Schematic of MOSAIC assays. Captured single molecule “immunosandwiches” are formed analogously to Simoa assays. DNA-conjugated streptavidin enables rolling circle amplification to be carried out, generating a strong local fluorescent signal on the bead surface, and then “on” and “off” beads are quantified by flow cytometry. f, 37H7::Nb5-5LL MOSAIC and Simoa assays in 10 previously-undetectable gastroesophageal (GE) cancer and healthy control patients. g, ORF1p is an early predictor of response in 19 gastroesophageal patients undergoing chemo/chemoradiotherapy; plasma was measured in all three second-generation Simoa assays before and during/post treatment; p<0.0001, Fisher’s Exact test h, Representative CT and PET-CT from patients in the cohort.
