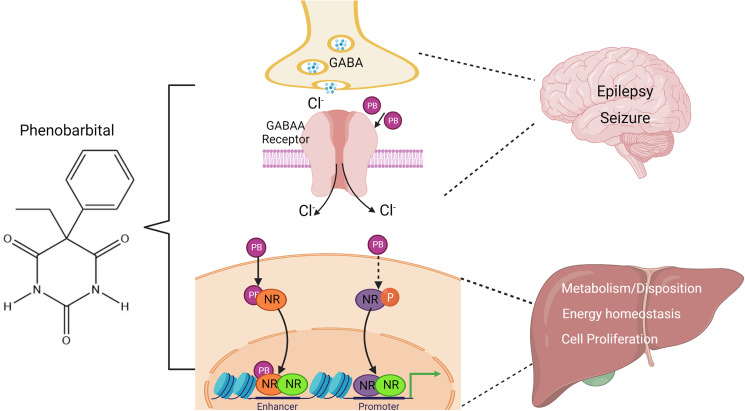
Fig. 1.
Effects of PB on the brain and liver. In the brain, PB enhances GABA responses in the neurons by binding to the GABAA-receptor in the postsynaptic membrane, which increases synaptic inhibition and elevates seizure threshold. In the liver, PB transactivates a number of nuclear receptors through both direct and indirect mechanisms to alter the expression of genes associated with drug metabolism and disposition, lipid and glucose metabolism, and cell proliferation.