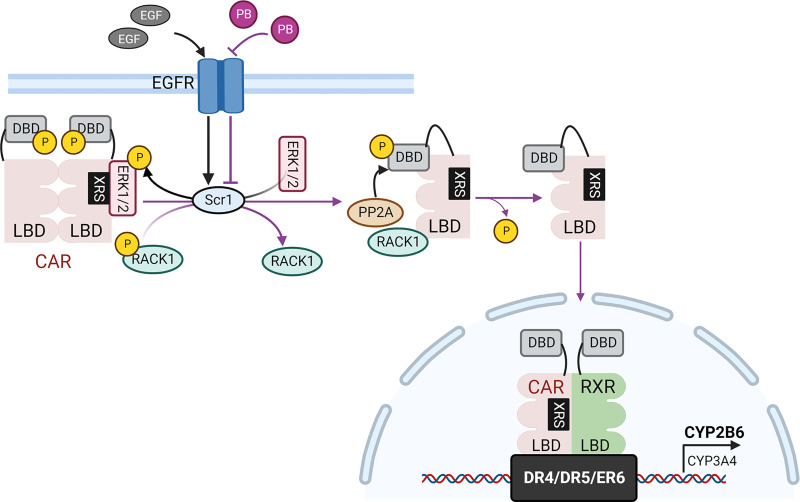
Fig. 2.
Mechanism of PB activation of CAR. PB antagonizes EGFR activity by directly binding to the receptor and competing with EGF, leading to decreased activity of the Scr kinase 1 which in turn reduces the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and RACK1. This signaling alteration results in dissociation of the nonactive CAR homodimer and release of ERK1/2. The dephosphorylated RACK1 recruits PP2A to the CAR monomer to remove phosphor from Thr-38. Subsequently, the dephosphorylated CAR translocates into the nucleus, forms a heterodimer with RXR, binds to response elements containing DR4, DR5, or ER6, and triggers the expression of target genes, such as CYP2B6 and CYP3A4.