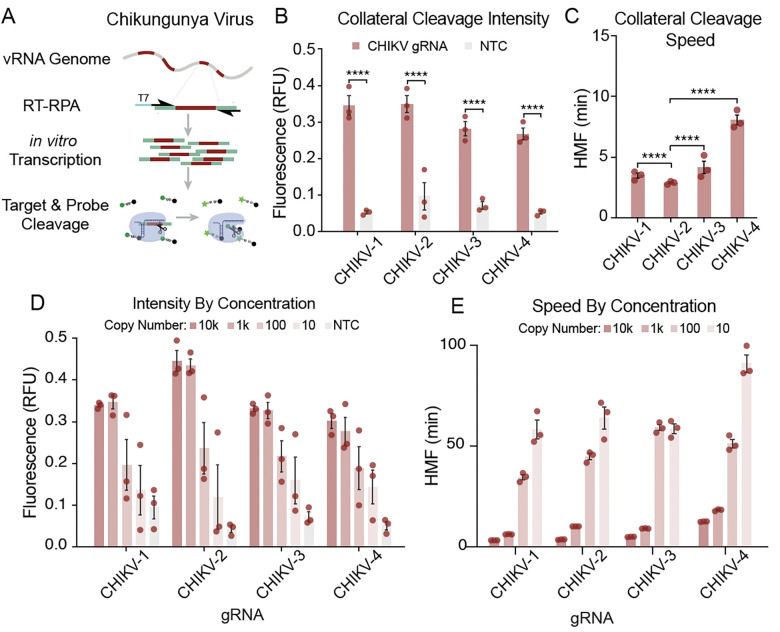
Fig. 3. Analysis of gRNA-dependent collateral activity targeting CHIKV.
(A) Schematic representation of the SENSR system used to determine the collateral cleavage activity of selected gRNAs. The detection protocol requires that the specific target sequences within the viral RNA are reverse transcribed (RT) into cDNA and amplified by RPA at 42 °C for 30 min. During amplification, a T7 promoter is incorporated into the 5′ terminus of the amplicons (T7, blue). In the next step, both in vitro transcription and CasRx collateral cleavage occur simultaneously. Finally, the recognition and cleavage of the target RNA sequence complementary to the gRNA induce collateral cleavage of bystander RNA molecules. Collateral cleavage of a modified probe conjugated to 6-FAM, and a fluorescence quencher facilitates readout by fluorescence. (B) Initial characterization of the collateral activity for each gRNA targeting CHIKV. SENSR analysis was performed against 10,000 copies/μL of the synthetic target. The fluorescence signal represents the background-subtracted signal. Statistical significance was calculated using Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (n = 3). (C) Collateral cleavage speed of each gRNA calculated using half-maximum fluorescence (HMF) analysis (see methods), where a lower HMF indicates faster collateral activity. Statistical significance was calculated using Tukey’s multiple comparison test (n = 3) (D) Intensity of signal from SENSR assay for each gRNA along a concentration gradient. The fluorescence signal represents the background-subtracted signal (n = 3). (E) Speed of cleavage along concentration gradient for each gRNA used to target CHIKV. The speed of collateral activity is represented using an HMF analysis (n = 3).