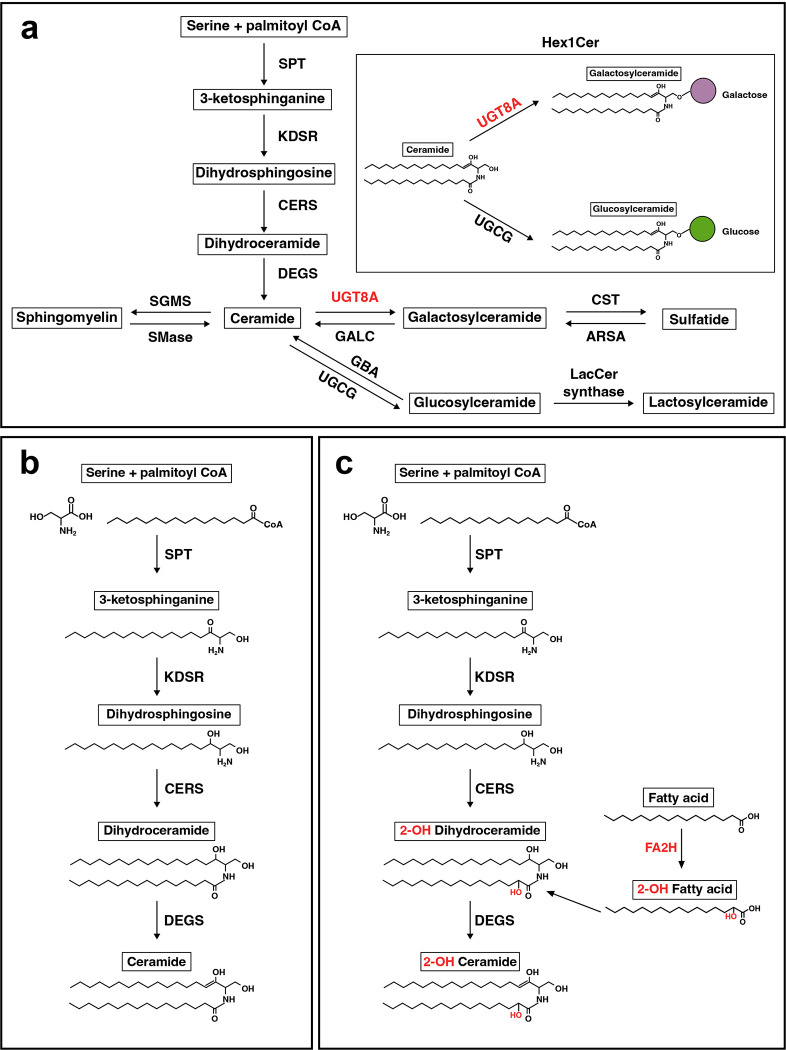
Figure 7. Simplified de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis pathway.
(a) Serine and palmitoyl CoA are condensed by serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) to generate 3-ketosphinganine. 3-ketophinganine is reduced to dihydrosphingosine by 3-ketodihydrosphingosine reductase (KDSR). Dihydrosphingosine is acetylated by ceramide synthases (CERS) and further desaturated by ceramide desaturase (DEGS) to generate ceramide. Ceramide is the substrate for generation of other sphingolipids (sphingomyelin, galactosylceramide, glucosylceramide, sulfatide, and lactosylceramide). Abbreviations: SGMS = sphingomyelin synthase, SMase = sphingomyelinase, UGT8A = UDP galactosyltransferase 8A, GALC = galactosylceramidase. CST = galactosylceramide sulfotransferase, ARSA = arylsulfatase, GBA = glucosylceramidase, UGCG = UDP-glucose ceramide glucosyltransferase, LacCer synthase = lactosylceramide synthase. (b) Biosynthesis of non-hydroxylated sphingolipids. (c) Biosynthesis of 2-hydroxy sphingolipids. Fatty acid 2-hydroxylase (FA2H) catalyzes hydroxylation of fatty acids in the C2 position, which can be incorporated into sphingolipid precursors (i.e., dihydroceramide) in the acylation step of de novo synthesis.