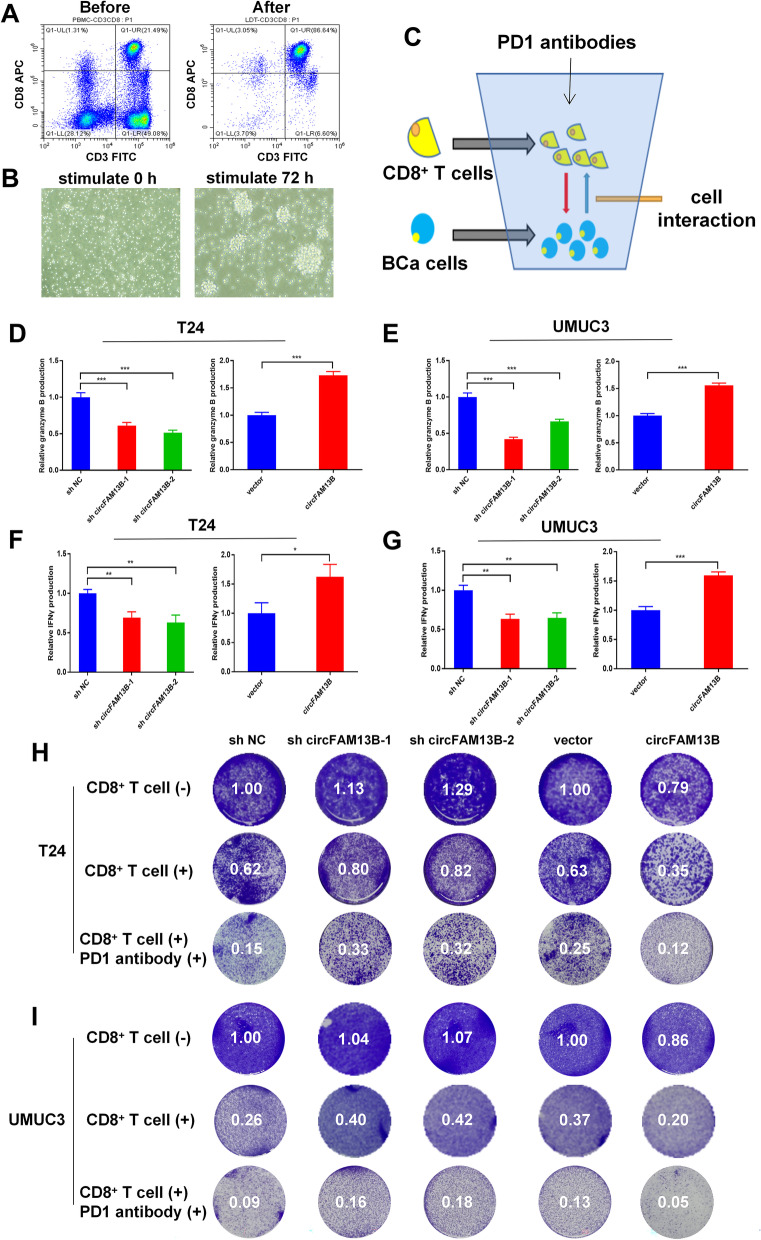
Fig. 2.
CircFAM13B promoted the effect of CD8+ T cells in vitro. A The efficiency of CD8 + cell screening was validated by flow cytometry by using CD3 and CD8 antibodies. B The morphology of CD8 + T cells before and after activation was observed under a microscope. C Schematic diagram of the co-culture model. D-E ELISA assays showed that CD8 + T cells co-cultured with circFAM13B knockdown T24 or UMUC3 cells secreted less granzyme B. CD8 + T cells co-cultured with circFAM13B overexpression T24 or UMUC3 cells secreted more granzyme B (***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test). F–G ELISA assays showed that CD8 + T cells co-cultured with circFAM13B knockdown T24 or UMUC3 cells secreted less IFN-γ. CD8 + T cells co-cultured with circFAM13B overexpression T24 or UMUC3 cells secreted more IFN-γ (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test). H The killing ability of CD8+ T cells and the immunotherapy sensitivity of BCa were inhibited when co-cultured with circFAM13B knockdown T24 cells. The killing ability of CD8+ T cells and the immunotherapy sensitivity of BCa were increased when co-cultured with circFAM13B overexpressed T24 cells. I The killing ability of CD8+ T cells and the immunotherapy sensitivity of BCa were inhibited when co-cultured with circFAM13B knockdown UMUC3 cells. The killing ability of CD8.+ T cells and the immunotherapy sensitivity of BCa were increased when co-cultured with circFAM13B overexpressed UMUC3 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 3