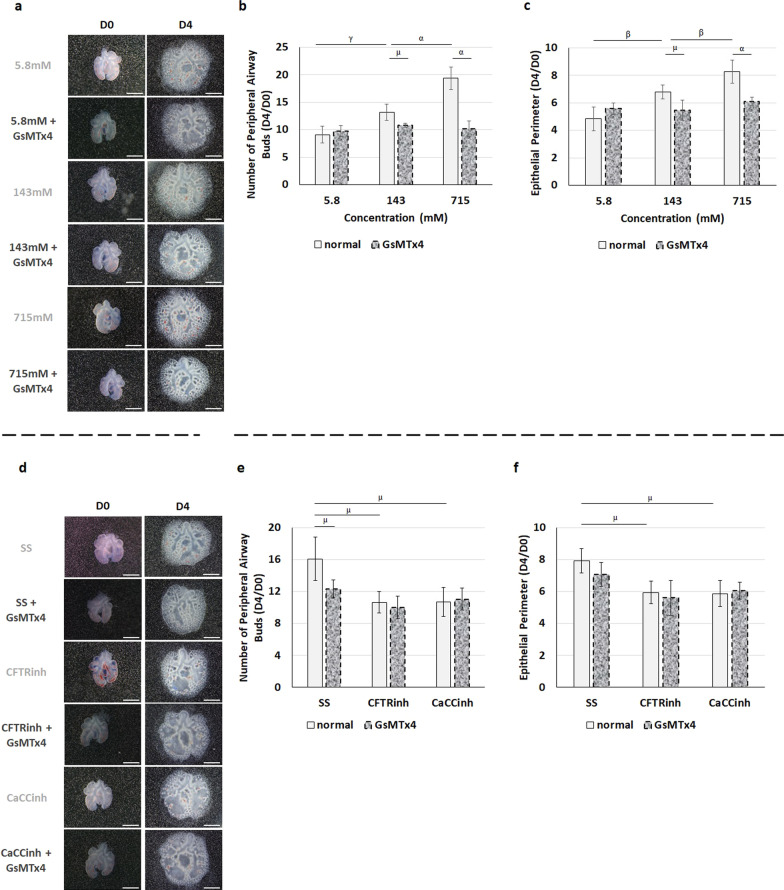
Fig. 4.
PIEZO1 and PIEZO2 mediate the effects of manipulating intraluminal chloride. a–c Upper panel represents the main cumulative effect of intraluminal injection of distinct chloride concentrations ([Cl−]) 5.8, 143, or 715 mM Cl− and the medium supplementation with GsMTx4 at day0 (D0) and day2 (D2). a Represents lung explants at D0 and D4 for the different [Cl−]. b, c Morphometric analysis of b peripheral airway buds and c epithelial perimeter. d–f Lower panel shows the additional effect of PIEZO1/2 inhibition after intraluminal injection of Cl− channels inhibitors: cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator inhibitor172 (CFTRinh) to CFTR; and calcium-dependent Cl− channel inhibitor A01 (CaCCinh) to CaCCs. d represents the fetal lung explants at D0 and D4 for the distinct Cl− channels inhibitors. e, f Morphometric analysis of e peripheral airway buds and f epithelial perimeter. 143 mM Cl− and standard solution (SS) identified the control condition for [Cl−] and Cl− channels inhibitors, respectively. White and dotted rectangles represent the medium supplementation with and without GsMTx4, respectively. n ≥ 4 were used per antibody/condition. Results are expressed as the ratio of D4 and D0 (D4/D0) and presented as mean ± SD. Symbols indicate the main effects and non-redundant interactions of the two-way ANOVA. p < α0.0001, β0.001, γ0.01, µ0.05