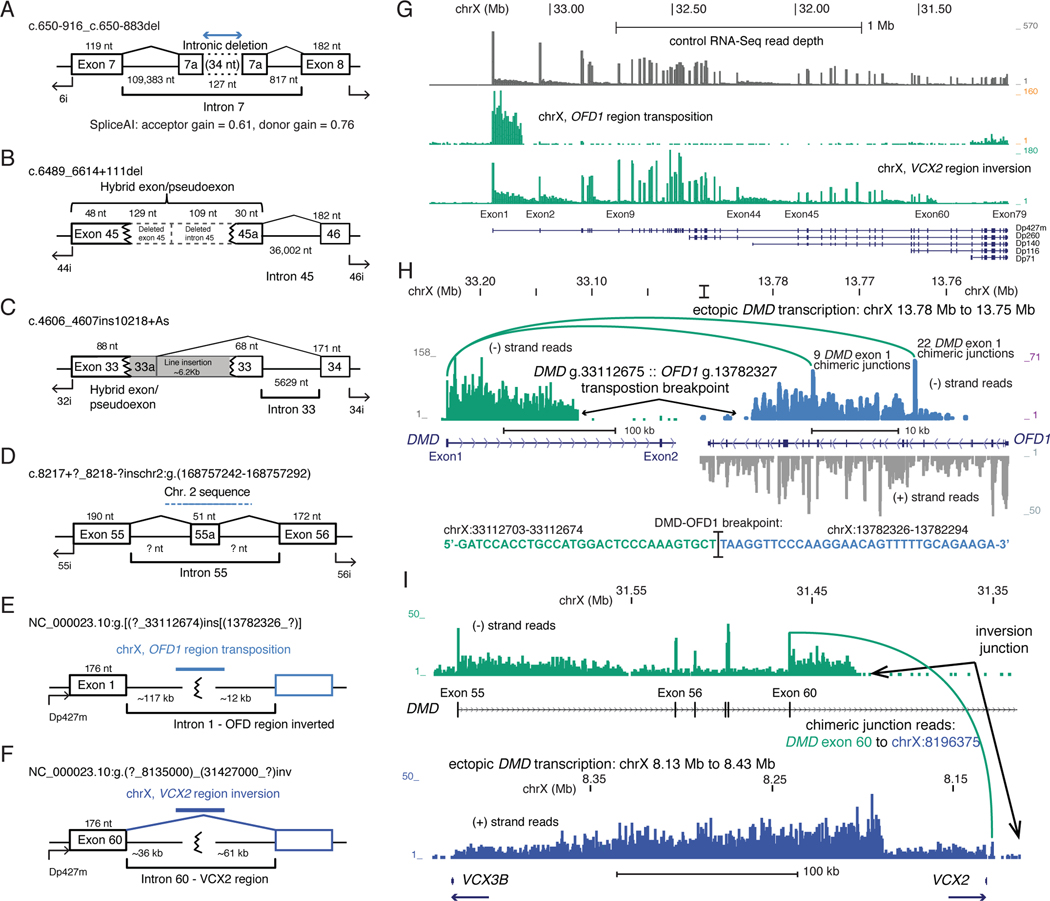
Figure 2. Type 2 and 3 DMD mutations.
Exon/intron diagrams for intronic deletions, insertions and chromosome level rearrangements. Mutations that (A) activate pseudoexon inclusion by a 34 nt. intronic deletion, (B) cryptic splice donor activation by a 238 bp. Deletion, or (C) a ~6.2 kb L1 retrotransposon insertion. Complex mutations due to (D) an inter-chromosomal transposition of a chr2 segment, (E) intra-chromosomal transposition of the chrX OFD1 region, and (F) a large, 23 Mb inversion between the VCX2–3 region at chrX:8.2 Mb and DMD intron 60 at chrX:31.4 Mb. (G) RNA-Seq read depth across the DMD region for the (E) and (F) mutations. (H) RNA-Seq coverage and exon junction reads that link DMD exon 1 with the OFD1 region, and the genomic sequence of the confirmed DMD intron 1 to OFD1 region junction. Strand-specific coverage is shown in the OFD1 regions, ectopic transcription on the minus strand shown in brown. (I) RNA-Seq coverage showing transcription from the DMD region and exon 60 junction reads supporting the inversion breakpoint junction (green), and ectopic transcription through the VCX2 – VCX3B region (blue).