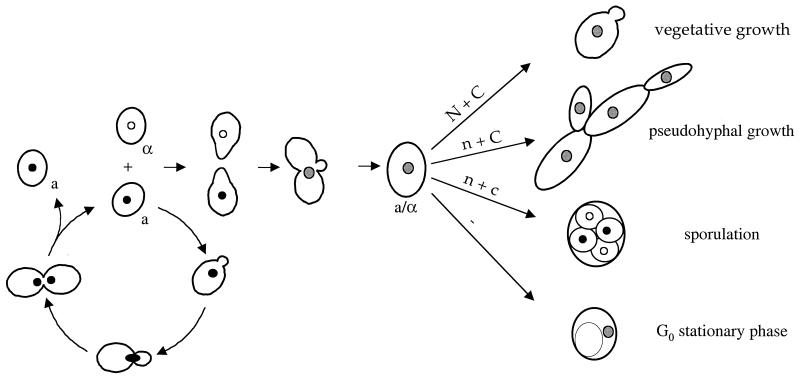
FIG. 1.
Life cycle of S. cerevisiae. Haploid yeast cells mate on rich medium. Diploid yeast cells adopt alternative fates depending on the availability of nutrients. N + C, abundant nitrogen and fermentable carbon source; n + C, limiting nitrogen and abundent fermentable carbon source; n + c, limiting nitrogen and nonfermentable carbon source; −, no nutrients.