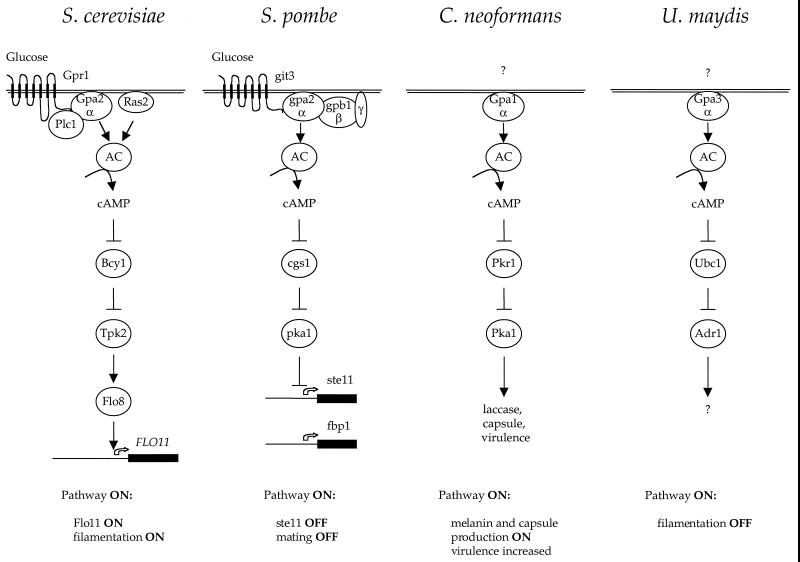
FIG. 15.
Role of cAMP in fungal morphogenesis. The nutrient-sensing receptor-G protein-cAMP-PKA signaling pathways are depicted. Two related receptors, Gpr1 and git3, play a conserved role in glucose sensing in S. cerevisiae and S. pombe; homologous receptors in C. neoformans and U. maydis remain to be identified. The receptors are coupled to a highly conserved Gα protein (variously called Gpa2, gpa2, Gpa1, and Gpa3), and the C-terminal domain that is known to interact with receptor has >80% sequence identify. The Gα protein is coupled to adenylyl cyclase, and cAMP regulates PKA. Targets of PKA largely remain to be identified but will likely include a variety of transcription factors. Note that cAMP functions to activate or inhibit development depending on the particular organism. AC, adenylyl cyclase.