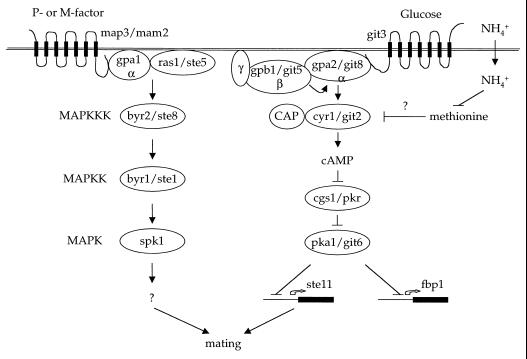
FIG. 5.
Signaling pathways regulating mating of S. pombe. Similar to S. cerevisiae diploid pseudohyphal growth, mating in S. pombe is regulated by two parallel signaling pathways. One responds to pheromones and involves a conserved MAP kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. The second is a nutrient-sensing pathway that, in the presence of abundant nutrients, stimulates cAMP production to repress ste11 expression and inhibit mating. CAP, cyclase-associated protein.