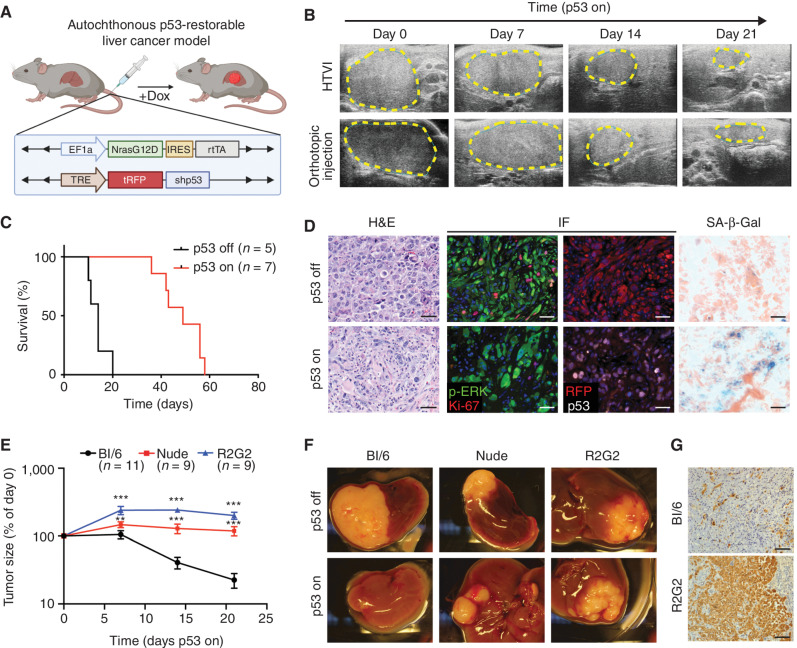
Figure 1.
A p53-restorable tumor model to study senescence immune surveillance. A, Generation of the p53-restorable, NRAS-driven mouse liver cancer model using the sleeping beauty transposon system delivered through HTVI. (Created with BioRender.com.) B, Representative ultrasonogram of HTVI and orthotopic injection liver cancer models at indicated time after p53 restoration. C, Survival analysis of mice in the HTVI model. D, Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), immunofluorescence (IF), and senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining of p53-suppressed (p53 off) and -restored (p53 on for 14 days) tumor sections generated from the HTVI model. Scale bars, 50 μm. E–G, Orthotopic injection of GFP-luciferase vector-transduced NSP tumor cells into the livers of immunocompetent and immunodeficient mouse strains. E, Tumor size change measured by ultrasound upon p53 restoration. R2G2, Rag2-Il2rg double-knockout mouse. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n e 9 for each strain. F, Representative macroscopic pictures at 21 days of p53 on or endpoint p53 off tumor. G, Representative IHC staining of GFP-labeled tumor cells at day 21 upon p53 restoration. Scale bars, 100 μm. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.