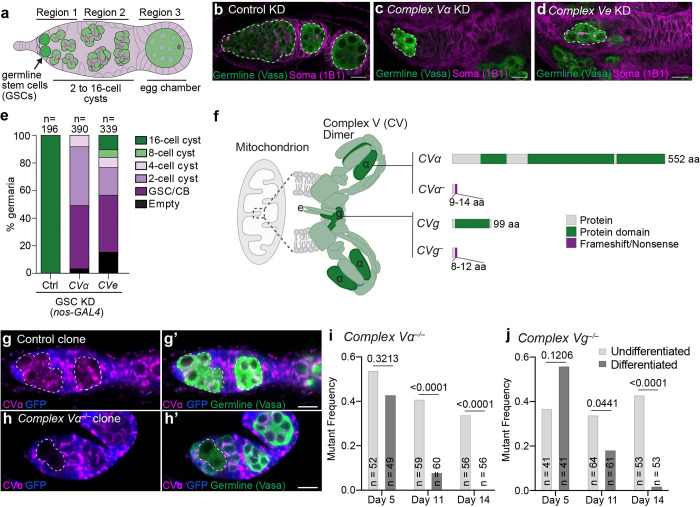
Fig 1. Complex V is essential for germline stem cell differentiation.
(a) Drosophila germarium. GSCs at the anterior tip of germaria asymmetrically divide and differentiate. The differentiating cell undergoes four rounds of mitosis with incomplete cytokinesis to generate a 16-cell interconnected cysts. The 16-cell cyst buds off as an egg chamber to further mature into an egg. (b-d) Representative images of 1-day old Control (mCherry) (b), CVα (c), and CVe (d) KD germaria driven by nos-GAL4. White-dashed lines mark the germline. (e) Quantification of the latest differentiation stage in germaria of indicated genotypes. RNAi were driven by nos-GAL4. Number of germaria scored is indicated above each bar. (f) Complex V dimer at the tip of mitochondrial cristae. CVα forms one of the main catalytic components of the complex. Subunits g and e are required for dimerization. Putative null alleles in α and g were generated. (g, h) Representative images of Control (g) and CVα (h) mosaic germaria 14-days after clone induction. Mutant GFP-negative clones are marked with the white-dashed lines. (i, j) Frequency of CVα (i) and CVg (j) mutant clones 5-, 11- or 14-days after clone induction. Undifferentiated: germline cells in region 1 including GSC, cystoblasts, 2-, 4- and 8-cell cysts. Differentiated: germline cells in region 2 containing 16-cell cysts. Number of germaria observed are given inside the bars. P-values were calculated using Fisher’s exact test. For all images scale bars represent 10 μm. For exact genotypes see S2 Table.