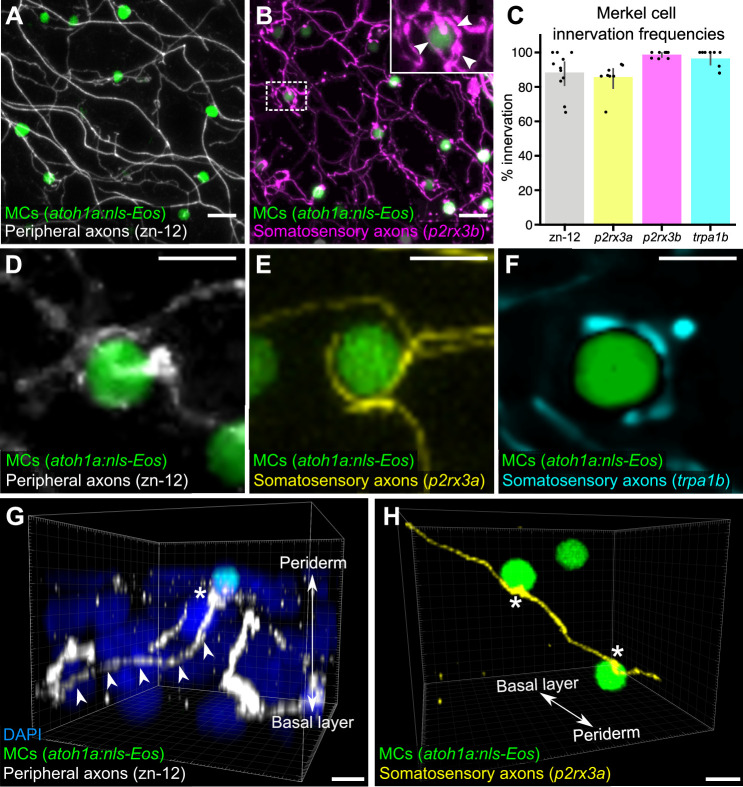
Figure 2. Somatosensory axons innervate Merkel cells (MCs) in the adult epidermis.
(A) Lateral confocal micrograph of the scale epidermis from an adult expressing an MC reporter immunostained for peripheral axons (zn-12). (B) Lateral confocal micrograph of the scale epidermis showing that somatosensory peripheral axons (Tg(p2rx3b:EGFP)) innervate MCs. Inset of dotted region shows axonal varicosities adjacent to an MC (arrowheads). (C) Quantification of MC innervation in the scale epidermis (17–30 mm standard length [SL]). Each dot represents measurements from an individual scale. Innervation frequencies: zn-12, 91% (284/311 cells; N=3 adults); Tg(p2rx3a>mCherry), 86% (196/228 cells; N=4 adults); Tg(p2rx3b:EGFP), 99% (225/228 cells; N=4 adults); Tg(trpa1b:EGFP), 96% (217/225 cells; N=9 adults). Error bars represent 95% CIs. (D–F) High-magnification confocal micrographs showing examples of somatosensory axons forming extended, ring-like contacts with MCs within the scale epidermis. (G) Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of an axon (zn-12 immunostaining, arrowheads) forming a bouton-like ending (asterisk) that terminates in close proximity to an MC. DAPI staining labels epidermal nuclei. (H) 3D reconstruction of a single somatosensory axon (Tg(p2rx3a>mCherry)) that forms en passant-like contacts (asterisks) with multiple MCs. Scale bars: 10 μm (A and B), 5 μm (D–H).