Fig. 3.
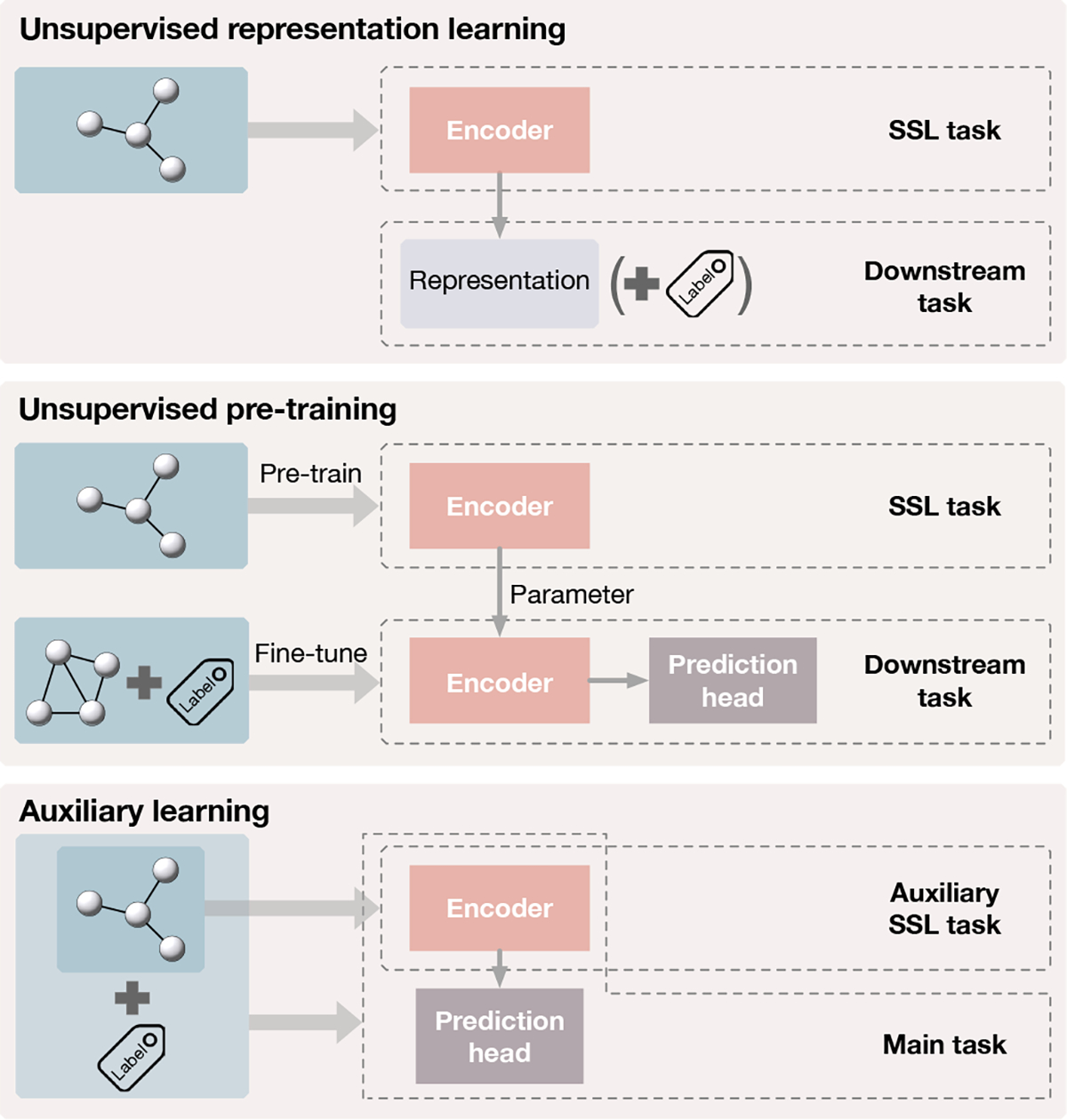
Paradigms for self-supervised learning. Top:in unsupervised representation learning, graphs only are used to train the encoder through the self-supervised task. The learned representations are fixed and used in downstream tasks such as linear classification and clustering. Middle: unsupervised pre-training trains the encoder with unlabeled graphs by the self-supervised task. The pre-trained encoder’s parameters are then used as the initialization of the encoder used in supervised fine-tuning for downstream tasks. Bottom: in auxiliary learning, an auxiliary task with self-supervision is included to help learn the supervised main task. The encoder is trained through both the main task and the auxiliary task simultaneously.
