Fig. 4.
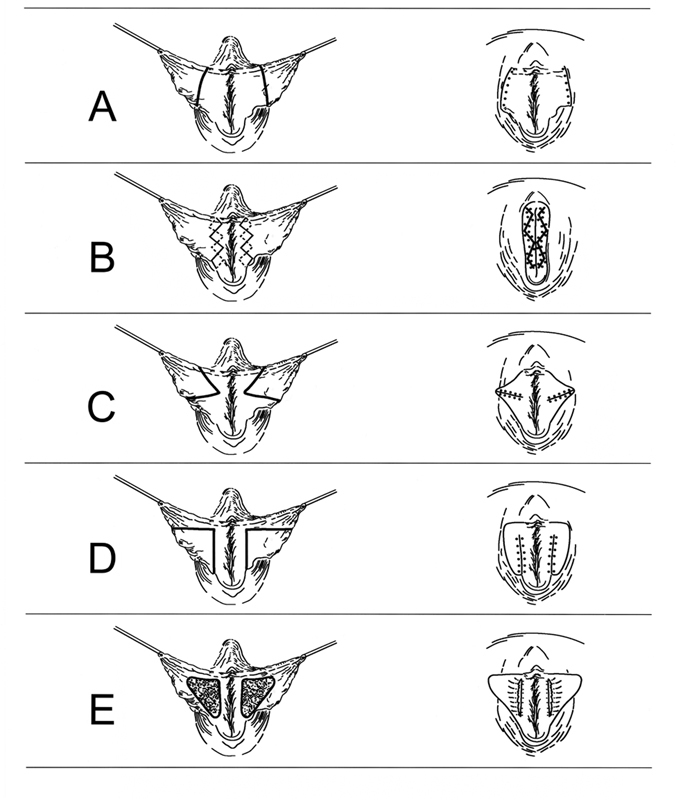
Edge resection, wedge excision, and central de-epithelialization are the three principal techniques for minor labial reduction. (A) Edge resection or trimming involves the straightforward amputation of protuberant tissues. Note that it additionally reduces the labial free rim length. (B) Straight amputation has been modified to a running W-resection to ensure a more robust and natural appearing rim after reduction. (C) Wedge excision involves the resection of a triangular part of skin at both the lateral and medial aspect of the labium minus. Note that it may correct a surplus of labial free rim length but only partly corrects labial width. (D) The initially central wedge excision has been modified to the dorsal wedge excision and anterior flap technique. Note that this modification also lowers the labial width and that the resulting scar runs less conspicuously along the base of the labium minus. (E) Central de-epithelialization involves the partial skinning of the medial and lateral aspects of the labium from its introital base, respectively, the interlabial sulcus outward. It may also be executed as a full-thickness resection or fenestration . Note that this will not reduce the labium free rim length.
