Figure 5.
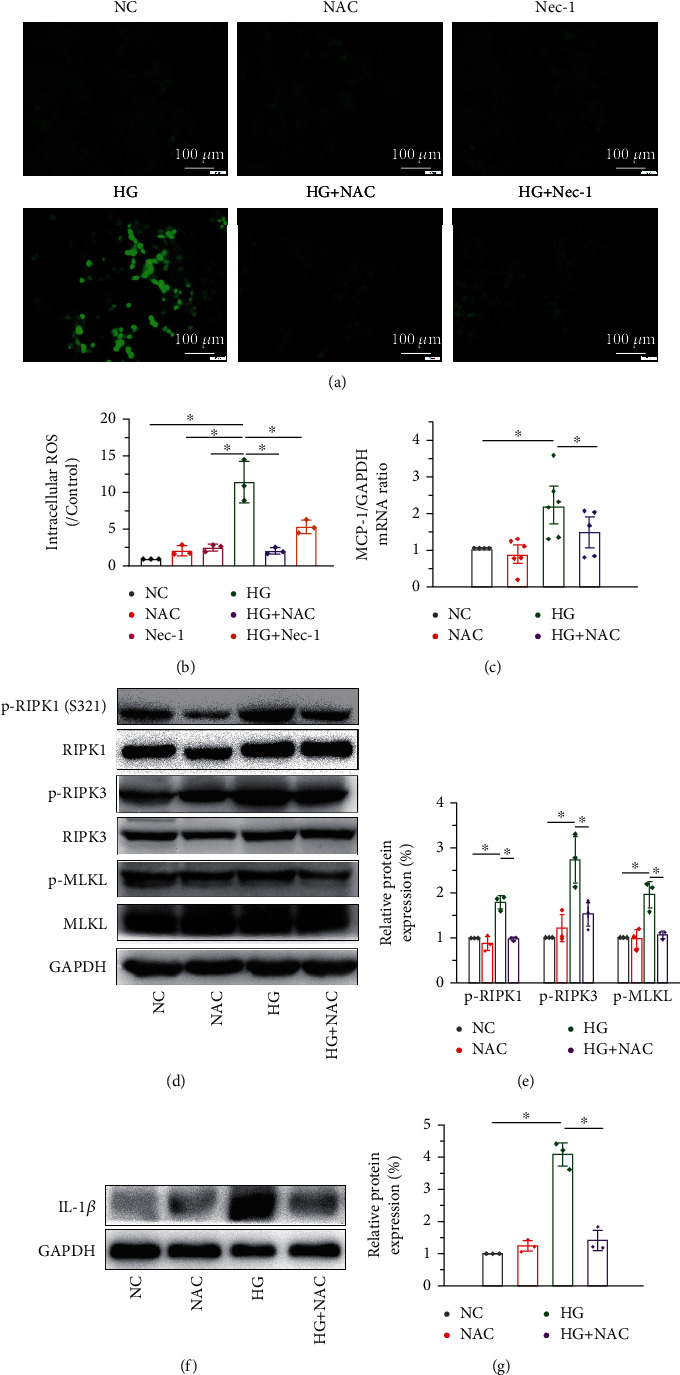
NAC treatment decreases necroptosis and inflammation by inhibiting RIPK1/RIPK3 signaling. (a, b) ROS levels increase significantly upon HG intervention and are effectively downregulated by NAC (2 mM for 48 h) and Nec-1 (50 μM for 48 h). Scale bar: 100 μm. Western blot analysis showing that HG activates the expression levels of the RIPK1 signaling pathway, including p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL compared to the control group. The addition of NAC effectively reduces necroptosis of the NRK-52E cells as NAC attenuates the upregulation of p-RIPK1 and p-RIPK3 (d, e). NAC treatment reduces the elevated mRNA level of MCP-1 induced by HG (c) and significantly decreases the level of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β) in vitro (f, g).
