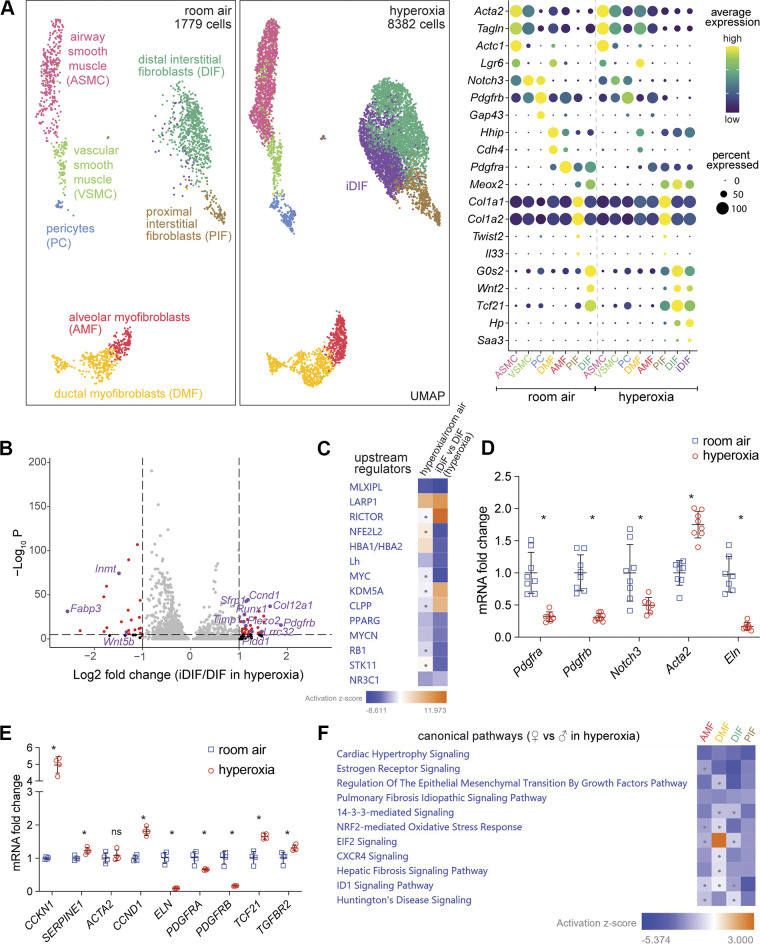
Figure 6.
New population of distal interstitial fibroblasts emerges in hyperoxia and shows sex-specific characteristics. A: UMAP of stromal cell showing seven clusters in RA (left) identified as DIF, PIF, AMF, DMF, PC, VSMC, and ASM. In hyperoxia (middle), a new cluster emerged labeled as iDIF (purple). Dot plot showing marker genes used for identification of each population (right). B: volcano plot shows gene expression differences between iDIF and DIF in hyperoxia. Significantly affected genes are shown in red, with some biological relevant genes highlighted in purple. C: IPA analysis revealing downregulation of MLXIPL and PPARG signaling in hyperoxia, whereas these two upstream regulators are even more repressed in iDIF vs. DIF. The dots in heat maps represent values that had a |Z-score| of <2 (nonsignificant). D: mouse whole lung qRT-PCR reveals downregulated expression of different stromal cluster marker genes, such as Pdgfra, pdgfrb, Notch3, and Eln, and upregulated Acta expression in hyperoxia. n = 8/group; *P < 0.02. E: immortalized human pulmonary fibroblasts (HPF-IM) in culture were exposed to 7 days of RA or hyperoxia (85% O2) and used to quantify CCKN1, SERPINE1, ACTA2, CCND1, ELN, PDGFRA, PDGFRB, TCF21, and TGFBR2 RNA expression by qRT-PCR. n = 4; *P < 0.05. F: IPA analysis indicating less pulmonary fibrosis signaling in female fibroblasts compared with male fibroblasts in hyperoxia. The dots in heatmaps represent values that had a |Z-score| of <2 (nonsignificant). IPA, Ingenuity Pathway Analysis; RA, room air.