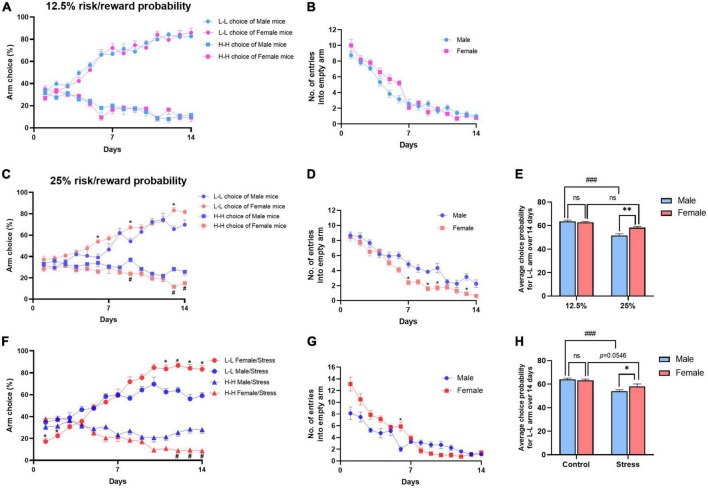
FIGURE 4.
Differences in decision-making between female and male mice. (A) Performance of different sex mice in the decision-making test under 12.5% probability. (B) Number of entries into empty arms. Not significant [F(1,20) = 2.454, P = 0.1329]. Dots show choice probability in each session. Repeat ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. Data shown as means ± SEM (n = 10-12). (C) Performance of different sex mice in the decision-making test under 12.5% probability. Repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. *P < 0.05 vs. the L-L arm choice in male group (post-hoc Tukey’s test, P = 0.0063 on day 6, P = 0.0057 on day 9, P = 0.0017 on day 13), #P < 0.05 vs. the H-H arm choice in male group (post-hoc Tukey’s test, P = 0.0019 on day 9, P = 0.0001 on day 13, P = 0.0479 on day 14). (D) Number of entries into empty arms. (E) L-L choice rate acquired over 14 days under the standard or double condition. Values are means ± SEM (n = 10–12). **P < 0.01 vs. male group under 25% ratio, ###P < 0.001 vs. male group under 12.5% ratio, n.s., not significant. (F) Performance of different sex mice in the decision-making after stress. Repeat ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. Data shown as means ± SEM (n = 8–12). *P < 0.05 vs. the L-L arm choice in male/stress group (post-hoc Tukey’s test, P = 0.0067 on day 1, P = 0.0146 on day 2, P = 0.0027 on day 11, P = 0.0002 on day 12, P = 0.0007 on day 13, P = 0.0005 on day 14), #P < 0.05 vs. the H-H arm choice in the male/stress group (post-hoc Tukey’s test, P = 0.0052 on day 12, P = 0.0052 on day 13, P = 0.0020 on day 14). (G) Number of entries into empty arms after stress. (H) L-L choice rate acquired over 14 days between the control and stress groups. Values are means ± SEM (n = 8–12). *P < 0.05 vs. stressed male group, ###P < 0.001 vs. control male group, n.s., not significant.