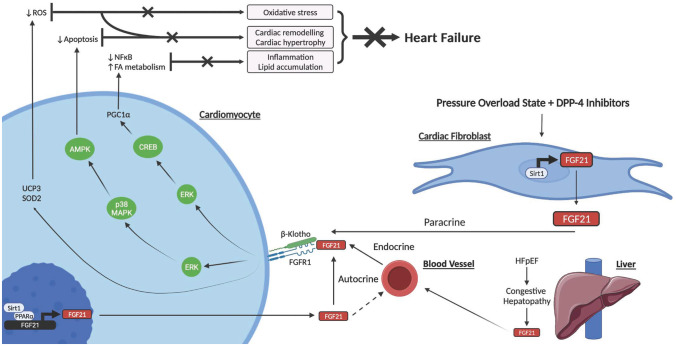
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram of postulated molecular mechanisms for FGF21 cardioprotection against HF development, outlining FGF21 expression, and its endocrine, autocrine, and paracrine action in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts [21, 24, 87]. Activation of the FGFR1/β-Klotho complex by FGF21 in cardiomyocytes stimulates the ERK pathway and phosphorylation of CREB protein, which increases PGC1 levels. PGC1a downregulates the NFkB pathway and upregulates FA metabolism which collectively attenuate cardiac inflammation and lipid accumulation. FGF21 additionally upregulates UPC3 and SOD2 and activates the ERK mitogen activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK)/AMPK pathway. UPC3 and SOD2 reduce ROS and thus oxidative stress, and AMPK decreases apoptosis. A decrease in apoptosis and oxidative stress is associated with attenuation of cardiac remodelling and cardiac hypertrophy. Collectively, these mechanisms protect against HF development. FGF21 is additionally produced in cardiomyocytes in response to cardiac stress via the SIRT1-PPAR-α pathway which may act in an autocrine manner and stimulate the surface FGFR1/β-Klotho complex or enter the blood stream and contribute to alterations in energy metabolism in extracardiac organs. In a pressure overload state combined with administration of DPP-4 inhibitors, cardiac fibroblasts express FGF21 via SIRT1 which may contribute to cardioprotection via a paracrine interaction with cardiomyocytes. In response to congestive hepatopathy in HFpEF, the liver likely expresses FGF21 which feeds back onto the heart as a compensatory protective mechanism. Abbreviations: FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; Sirt1, sirtulin 1; PPAR α, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α; FGFR1, fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; CREB, cAMP responsive element binding; PGC1a, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1-α; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NF- B, nuclear factor B; p38 MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; FA, fatty acid; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; UCP3, uncoupling protein 3; SOD2, superoxidase dismutase 2