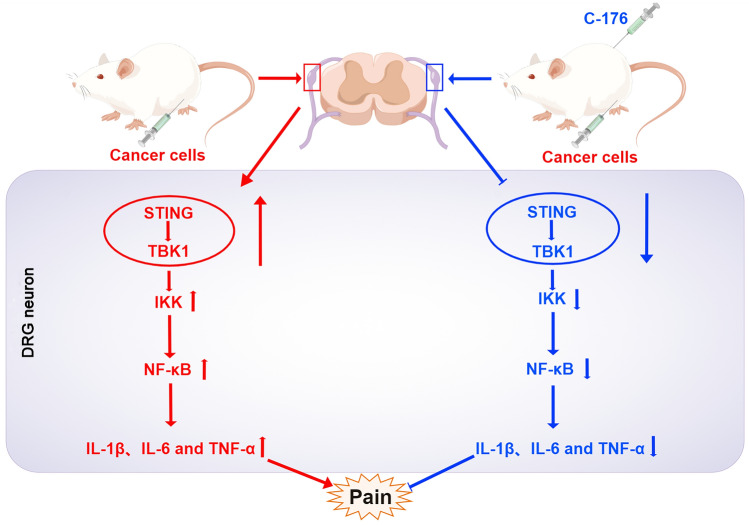
Fig. 9.
Schematic summarizing the mechanism by which STING promotes BCP. The expression level of STING in the DRG was significantly increased in BCP rats, sequentially activating the TBK1/IKK/NF-κB/proinflammatory factor axis to promote neuroinflammation and eventually induce enhanced BCP. After intraperitoneal injection of C-176, the level of STING in the BCP rats was decreased, and the TBK1/IKK/NF-κB/proinflammatory factor signaling pathway was then inhibited. Therefore, STING inhibition in the DRG relieved peripheral sensitization, which ultimately alleviated BCP. This figure was drawn with Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) (color figure online)