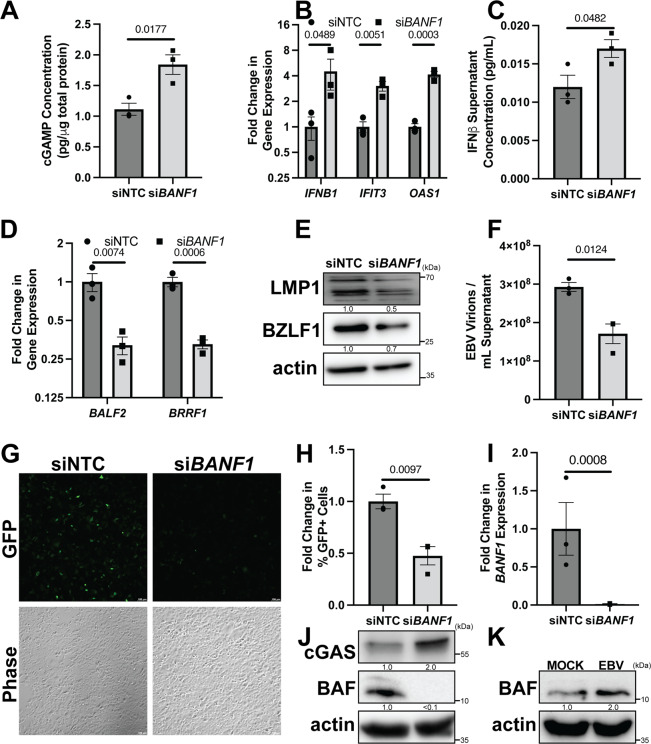
Fig. 6. BAF facilitates EBV reactivation from latency in epithelial cells.
AGS-EBV cells were transfected with NTC or BANF1 targeting siRNA for 48 h prior to the addition of 5 ng/mL TPA. A Cell lysates were collected at 72 h post-TPA treatment and analyzed by 2’3’-cGAMP ELISA. B Cells were harvested and RNA was isolated at 48 h post-TPA treatment. RT-qPCR was subsequently performed to determine ISG mRNA expression levels. C Culture supernatant was harvested at 72 h post-TPA treatment and analyzed by IFNβ ELISA. D Cells were harvested and RNA was isolated at 72 h post-TPA treatment and RT-qPCR was performed to quantify viral mRNA transcripts. E Cell lysates were prepared at 72 h post-TPA treatment and analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibodies. F Culture supernatants were harvested at 72 h post-TPA treatment and DNase treated prior to DNA extraction. DNase-resistant EBV genomes were quantified by real-time qPCR to assess viral load. G At 72 h post-TPA treatment, culture supernatants were used to infect naive HEK293 cells. Forty-eight h post infection, GFP + infected cells were analyzed by fluorescent microscopy. H Cells were also quantified by flow cytometry. I Cells were harvested for RNA at 48 h post-siRNA transfection and subsequent RT-qPCR was performed to quantify BANF1 mRNA transcripts. J Cell lysates were prepared at 48 h post-siRNA transfection and analyzed by western blotting with the indicated antibody. K Naive AGS cells were infected with equivalent units of concentrated cell-free EBV or PBS (mock). Cell lysates were prepared 6 h post-infection and analyzed by western blotting. P values are the result of two-tailed Student’s T tests unless otherwise specified. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean of three independent biological replicates. Source data are provided as a source data file.