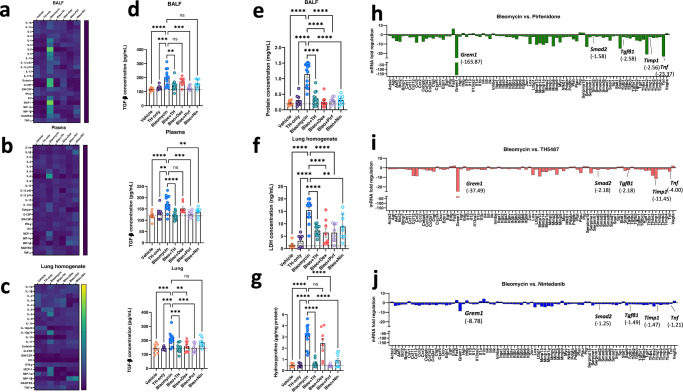
Fig. 4. Significantly decreased cytokine levels following TH5487 administration, with accompanying reduction in markers of lung damage.
Heatmaps (a–c) showing the differences in cytokine levels, as measured by multiplex assay, in murine bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), plasma, and lung homogenate (mean-normalized values shown, with yellow indicating high values and blue indicating low values). Cytokine values were compared to the vehicle/Bleo group using a one-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.0001). ns: not significant. TGF-β1 ELISA (d) conducted on murine BALF, plasma, and lung homogenate revealed significantly decreased TGF-β1 levels in all three murine sample types with values compared to the vehicle/Bleo group using a one-way ANOVA: Bleo vs Bleo+TH (BALF: P = 0.0022; plasma: P < 0.0001, Lung homogenate: P = 0.0001). Data are presented as means ± SEM (d–g). Murine albumin content (e) and Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (f) were measured in BALF samples as markers for lung damage and plasma leakage, with TH5487 treatment significantly decreasing both albumin content (P < 0.0001) and LDH levels in the BALF (P = 0.0022) compared to the vehicle/Bleo group. g Murine lung collagen content was measured using a hydroxyproline assay with TH5487 significantly reducing collagen levels (P < 0.0001) compared to Bleo control lungs (d–g: (Bleo n = 14, Bleo/TH n = 13, Bleo/Dex n = 8, Vehicle n = 8, TH only n = 8, Bleo/Pirf n = 8, Bleo/Nin n = 8). h–j qRT-PCR arrays specific for mouse fibrotic genes were used to analyze murine lung samples (n = 5 pooled samples) following treatment using TH5487 (TH), nintedanib (Nin), and pirfenidone (Pirf). Source data are provided as a Source data file.