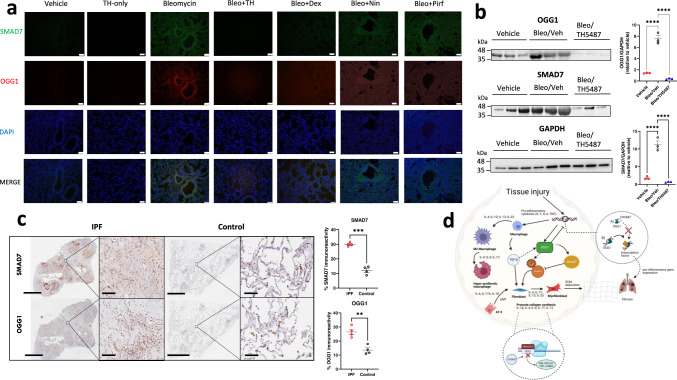
Fig. 8. Lower expression of OGG1 and SMAD7 are seen in both TH5487-treated mice and human explanted control lungs.
a Murine lung immunofluorescence analysis showed decreased levels of immunoreactivity for OGG1 (red)/SMAD7 (green) in TH5487 (TH)-treated mice compared to bleomycin (Bleo) controls (DAPI, blue; scale bar = 50 μm), results shown from 3 independent experiments, b with mouse lung homogenate samples analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using rabbit antisera specific to OGG1 and SMAD7 (protein levels quantified inset n = 3 per treatment; statistical analyses were conducted using a one-way ANOVA (****P < 0.0001 for comparisons between all groups tested)). Data are presented as means ± SEM (b, c). c This result translated into human patient samples, with healthy control lung tissue displaying significantly decreased levels of OGG1 and SMAD7 immunoreactivity (brown staining; P = 0.0024 and P = 0.0002, respectively), as compared using an unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (two-sided), n = 4 patients per group. Scale bar = 6 mm and 100 μm for inset images. d Excessive OGG1 production facilitates pro-inflammatory gene expression, promoting inflammatory cell recruitment, leading to further exacerbation of the fibrotic lung environment. In addition, OGG1 promotes the phosphorylation of SMAD 2/3 by SMAD7 interaction, promoting TGF-β-driven FMT and EMT and excessive ECM deposition. Therefore, decreased OGG1 expression and binding to DNA by TH5487 inhibits downstream pro-inflammatory gene expression and pulmonary fibrosis. In this study, OGG1 and SMAD7 levels were both reduced after the administration of TH5487, as shown by SDS-page/immunoblotting. Source data are provided as a Source data file. Elements of this figure were created with BioRender.com.