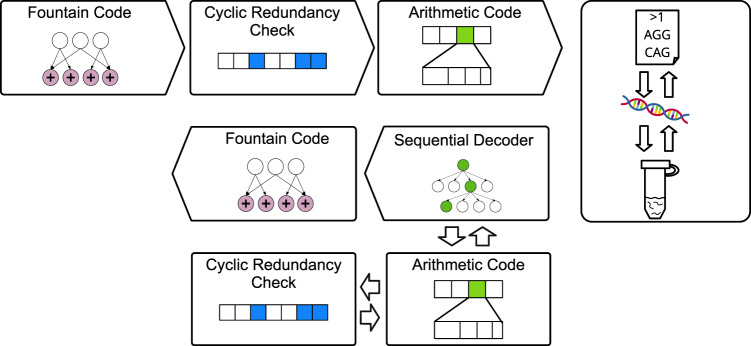
Fig. 6. Overview of the DNA storage workflow using DNA-Aeon: Input data is encoded and packetized using the NOREC4DNA Raptor fountain code, followed by periodic insertion of an 8-bit CRC checksum, including a final CRC to protect the end of the packet.
The packets are then encoded in parallel using the arithmetic code, using a constraint-free codebook. The channel (right side of the figure) represents the DNA synthesis, storage, and sequencing of the encoded data. The channel output packets are decoded in parallel by the inner, sequential decoder. The sequential decoder stores the states of the arithmetic code as nodes. In periodic intervals, a CRC check of the data that was decoded since the last CRC checksum is performed. The fountain code then uses the packets with the highest final Fano metric to recover the original input data.