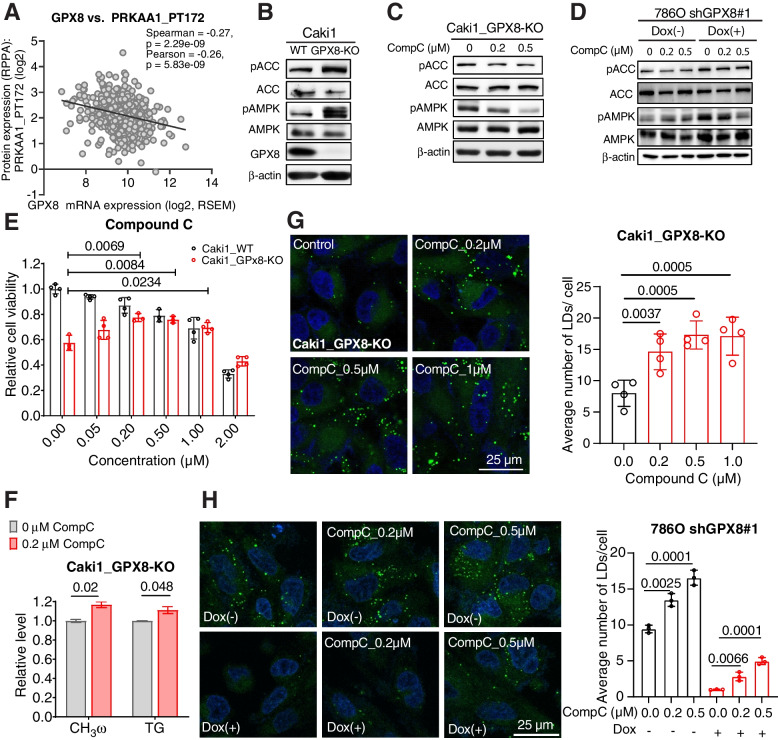
Fig. 4.
GPX8 enhances lipid accumulation by inhibiting AMPK. A, Correlation between GPX8 mRNA expression and phosphorylated AMPKα1 (PRKAA1_PT172) level obtained from Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPA) data of TCGA-KIRC dataset. B-C, Western blot analysis for phosphorylated and total forms of ACC (Ser 79) and AMPK α1 (T183) α2 (T172) in GPX8 WT and KO cells (B) and effects of compound C on GPX8-KO Caki1 cells for 2 days (C). D, shGPX8 786O cells were incubated with or without doxycycline (100 ng/mL) for 3 days. These cells then were treated with compound C in a range of concentration for 2 days. Western blot analysis for the effects of compound C on phosphorylated forms of ACC (Ser 79) and AMPK α1 (T183) α2 (T172). E, Relative cell viability of WT and GPX8-KO Caki1 cells upon treatment of different concentrations of compound C for 3 days. F, FA de novo synthesis and triacylglycerol synthesis in GPX8-KO with and without compound C (0.2 µM) as in Fig. 3H. G, Representative pictures from quadruplicates (left) of neutral lipid BODIPY 493/503 staining of GPX8-KO Caki1 cells treated with different concentrations of compound C for 3 days. Quantitation of the lipid droplet (right) (n = 4) as in Fig. 3F. H, Representative pictures from triplicates (left) and quantitation (right) for lipid staining for shGPX8 786O cells as in Fig. 3F (n = 3). Data presented in panels (E), (F), (G), and (H) are means ± SD (n ≥ 3). P-values were determined by unpaired t-test