Figure 5.
Refined association between SCRIB and white-matter integrity of tapetum
The Genebass browser provides views of the full dataset, including all quality control metrics and association statistics.
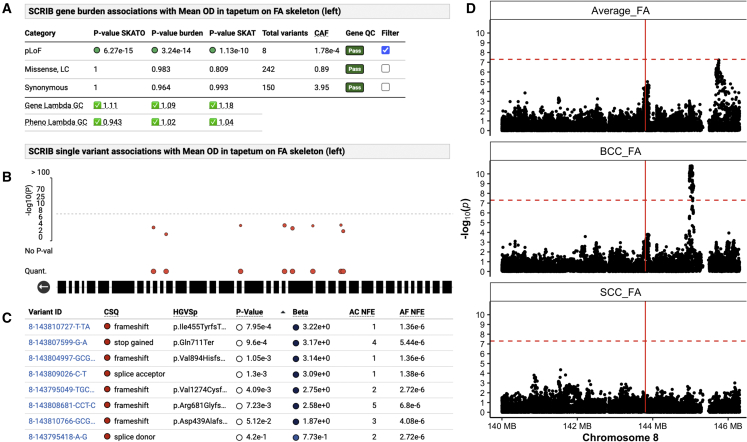
(A) The summary of association information between pLoF variants in SCRIB with mean orientation dispersion (OD) index in tapetum on fractional anisotropy (FA) skeleton (from diffusion magnetic resonance imaging [dMRI] data).
(B) A rare variant Manhattan plot of 8 rare pLoF variants is shown.
(C) Details for the component variants are shown in a table, including their functional consequence (CSQ), a detailed protein-coding annotation (HGVSp), and the association p value and beta, as well as frequency information (AC, allele count; Hom, number of homozygotes; AN, allele number; AF, allele frequency). Each component pLoF variant in scrib has a positive beta value, and in aggregate, these variants show an association at p = 6 × 10−15 (A).
(D) A Manhattan plot of a previous GWAS29 of FA averaged across brain regions (top), body of corpus callosum (middle), and splenium of corpus callosum (bottom). Horizontal dashed line indicates a GWAS genome-wide significance threshold (5 × 10−8), and vertical line indicates the location of SCRIB.