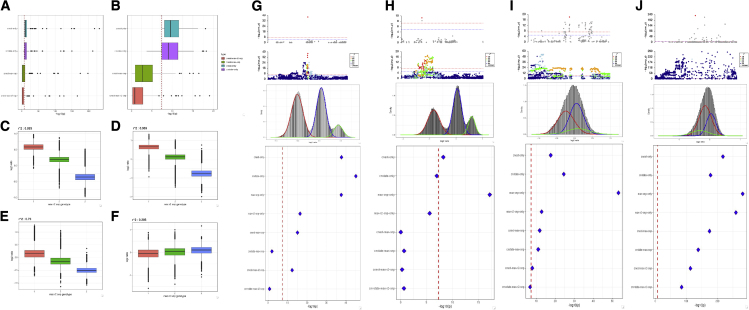
Figure 5.
Competitive models for CNV and SNPs using copy number estimates, copy number genotypes, and joint models including SNP genotypes from the most highly correlated SNP or the SNP with the highest association signal for the same trait within 1 Mb
(A) Minus log10 p values for four different models: CNest only, copy number estimates only; cnstate only, copy number genotypes (three-component mixture model) only; CNest-max-snp, joint model with copy number estimates and the SNP with the highest association signal for the same trait within 1 Mb; CNest-max-r2-snp, joint model with copy number estimates and the most highly correlated SNP within 1 Mb.
(B) Zoomed in view of (A) restricting the x axis to a maximum −log10 p value of 20.
(C–F) SNP genotypes from the most highly correlated SNP against the copy number estimate (log2 ratio) for four individual exon-level association signals, further details of which are shown in (G)–(J).
(G–J) Finer-grain details for joint models of four exon-level copy number association signals; top panel shows the copy number estimate association signal with the lead exon highlighted in red, second panel shows the SNP genotypes association signal from SNP GWAS tests in the same samples and trait colored by the r2 of SNP genotypes against the lead exon signal from the copy number GWAS (CN-GWAS), the third panel shows the copy number estimate (log2 ratio) of the lead exon association from the CN-GWAS fitted using a three-component mixture model to define copy number genotypes, and the fourth panel shows the −log10 p value from eight different types of association model: cnstate-only, cnstate-only, max-snp-only, max-r2-snp-only, CNest-max-snp, cnstate-max-snp, CNest-max-r2-snp, and cnstate-max-r2-snp.