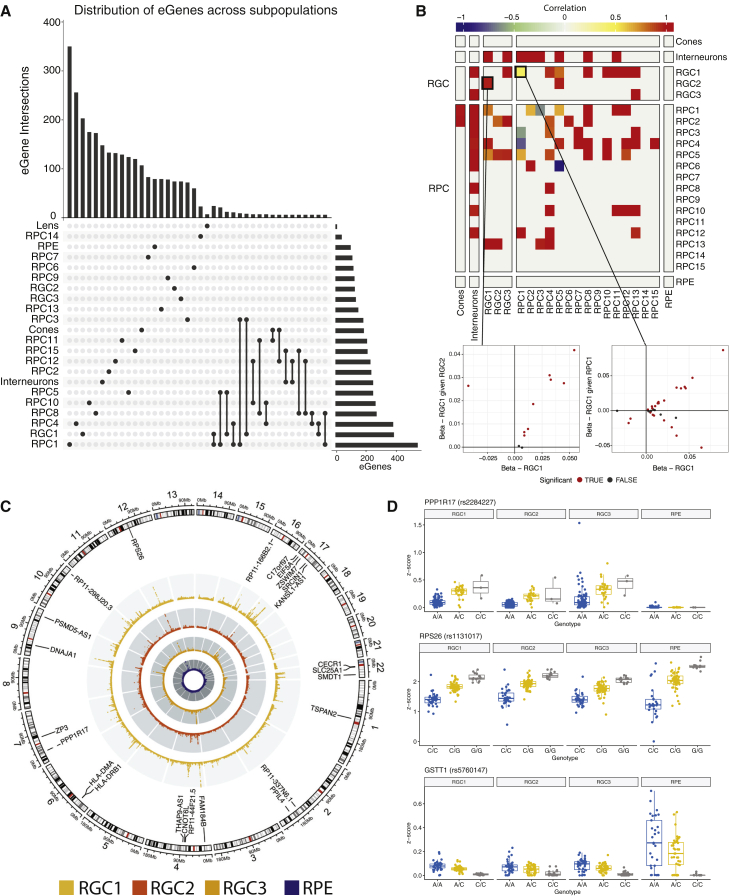
Figure 3.
Cell subpopulation-specific eQTLs—Summary of eQTLs specific to cell subpopulations
(A) Minimal overlap of genes with significant eQTLs (eGenes) show that they are predominantly subpopulation specific.
(B) For eGenes present in more than one subpopulation, we compared the allelic effect from the original lead eQTL in one subpopulation with the allelic effect after conditioning the eQTL with an eSNP for the same eGene from another subpopulation. The heatmap represents the pairwise correlations between allelic effects of each tested subpopulation. The scatterplots represent the allelic effects—measured as beta—in RGC1 conditioned against RGC2 and RGC1 conditioned against RPC1. The original beta values are plotted on the x axis, and the conditioned beta values are plotted on the y axis. The color of the points shows if the change in allelic effect was significant (red).
(C) Chromosomal map of significant loci in RGC subpopulations RGC1 (light orange), RGC2 (red), RGC3 (dark orange), and RPE (blue). Loci were labeled significant if FDR <5 × 10−8. Table S8 contains full details of significant loci.
(D) Relationships between genotype and Z score for examples of common eQTL (RPS26 [rs1131017] and GSTT1 [rs5760147]) and RGC-exclusive eQTL (PPP1R17 [rs2284227]) in comparison with corresponding loci within RPE subpopulation.