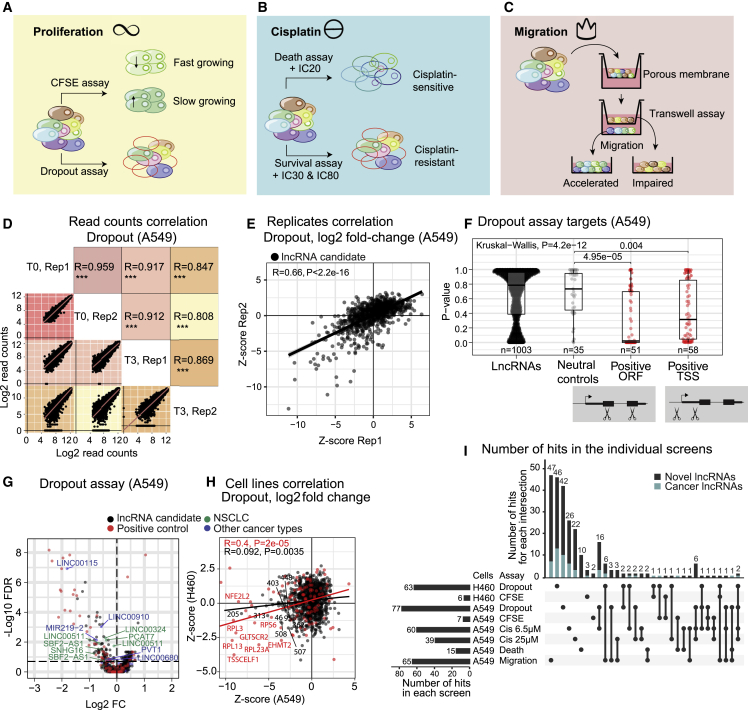
Figure 2.
Adapting CRISPR screens to cancer hallmarks
(A) Proliferation: the strategy employs complementary negative (dropout) (growth-promoting lncRNAs’ pgRNAs are depleted) and positive (CFSE dye) (growth-promoting lncRNAs’ pgRNAs are enriched) formats.
(B) Cisplatin sensitivity: another complementary strategy is employed. In the negative (dropout) “survival” screen, cells are exposed to high cisplatin doses (IC30, IC80). Resistance-promoting lncRNAs’ pgRNAs will be depleted in surviving cells. In the positive “death” screen, cells that die in response to low cisplatin concentration (IC20) are collected, and enriched pgRNAs identify resistance-promoting lncRNAs.
(C) Migration: cells that are capable/incapable of migrating through a porous membrane over a given time are separately collected. Migration-promoting lncRNAs are identified via their pgRNAs’ enrichment in migration-impaired cells.
(D) Read counts correlation of the dropout assay in A549. Log2 of the read counts (T3: 3 weeks; T0: time point zero). Z score-transformed log2 values. Statistical significance: Pearson correlation.
(E) lncRNA candidates (black) correlation between biological replicates of the dropout screen in A549 cells. Data presented as Z score-transformed log2FC values (T3/T0). Statistical significance: Pearson correlation.
(F) P-value distribution of lncRNA candidates and neutral and positive controls in A549 dropout screen. Protein-coding genes used as positive controls are analyzed separately using pgRNAs targeting the ORF and TSS. Statistical significance: Wilcoxon test (pairwise comparisons) and Kruskal-Wallis (global differences).
(G) A549 dropout screen. The horizontal line indicates the cutoff for hits at FDR <0.2. Previously published lncRNAs in NSCLC and other cancers are labeled in green and blue, respectively.
(H) Comparison of A549 and H460 dropout screens (four points removed for clearer visualization, statistical significance estimated on all the data points using Pearson correlation).
(I) Analysis of lncRNA hits that have potential impacts on the described phenotypes by screens in A549 and H460 cells with FDR <0.2. The light blue bat indicates the fraction of previously discovered “cancer lncRNAs” from the CLC2 database.16