Figure 6.
Complex event visualization
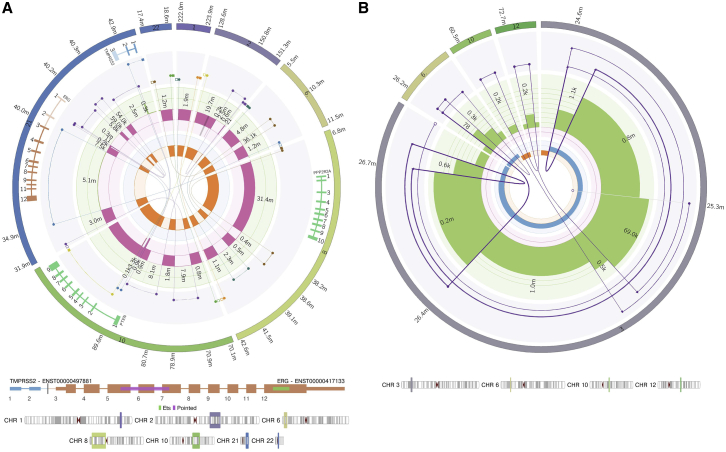
(A) Chromoplexy-like cluster formed from 19 break junctions across seven chromosomes in HMF001596B, a prostate tumor. The rearrangement leads to three distinct putative drivers in a single event, including a chained TMPRSS2-ERG fusion with two hops; a loss of heterozygosity for PPP2R2A, which also has a stop-gained point mutation (not shown); and an intronic homozygous disruption of PTEN.
(B) Breakage fusion bridge event affecting the P arm of chromosome 3 in the melanoma cell line COLO829T. The predicted derivative chromosome has a copy number of two and can be traced outwards starting from the centromere on chromosome 3, traversing two simple foldbacks and two chained foldbacks and finishing on a single breakend at chr3:25.3M, which from the insert sequence can be inferred to be connected to a centromeric satellite region (likely chromosome 1, which has a copy number gain of two over the centromere from P to Q arm and which appears to be connected to chromosome 3 in unpublished SKY karyotype figures; http://www.pawefish.path.cam.ac.uk/OtherCellLineDescriptions/COLO829.html). One chained foldback at chr3:26.4M includes a genomic shard from chr6 of approximately 400 bases, which has itself been replicated and internally disrupted by the foldback event. The other chained foldback at chr3:25.4M includes two consecutive genomic shards inserted from chromosome 10 and 12 of approximately 200 bases each.