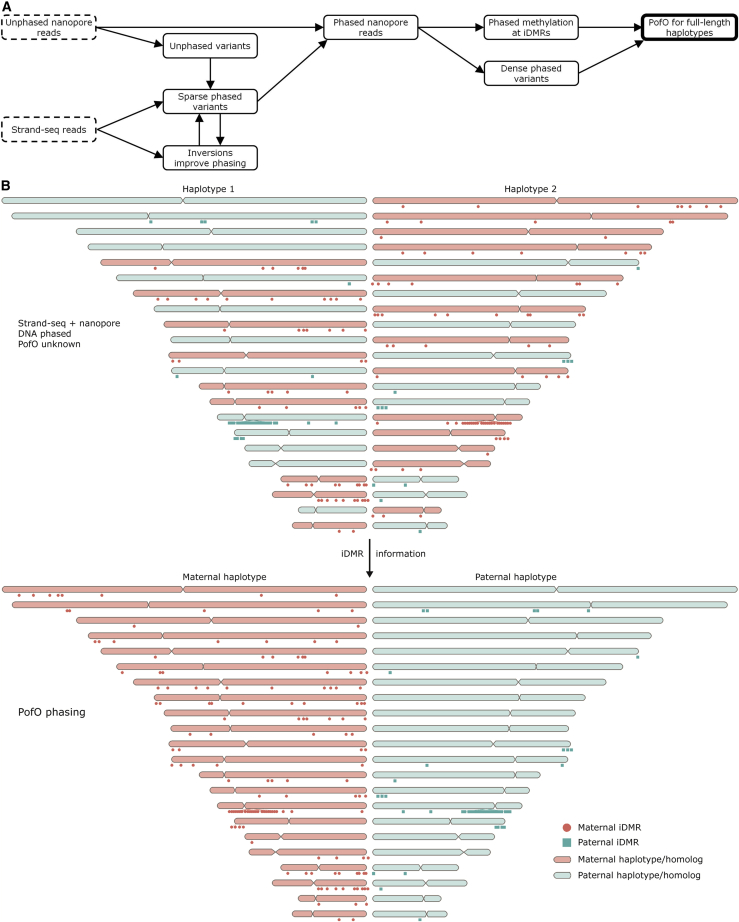
Figure 1.
Overview of the parent-of-origin (PofO) phasing method
(A) The inputs for the workflow are nanopore long reads and data from single-cell Strand-seq libraries. Nanopore data are used to call variants, some of which are phased with Strand-seq in an inversion-aware manner. These phased variants are then used to phase the nanopore reads, which are used to phase more variants and DNA methylation. Finally, the DNA methylation status of iDMRs is used to identify the PofO for each homologous chromosome.
(B) Without examining DNA methylation, Strand-seq and nanopore reads can be combined to construct chromosome-length haplotypes,14,16 but the assignment of each homolog (i.e., chromosome-length haplotype) to haplotype 1 or haplotype 2 (HP1 or HP2) is random with respect to its PofO, as shown by this cartoon. However, iDMRs can be used to distinguish maternal and paternal homologs. Lollipops mark the locations of all 144 maternal iDMRs used in this study (methylated on the maternal homolog) and all 48 paternal iDMRs.
For iDMR names and locations shown relative to cytobands, see Figure S7.