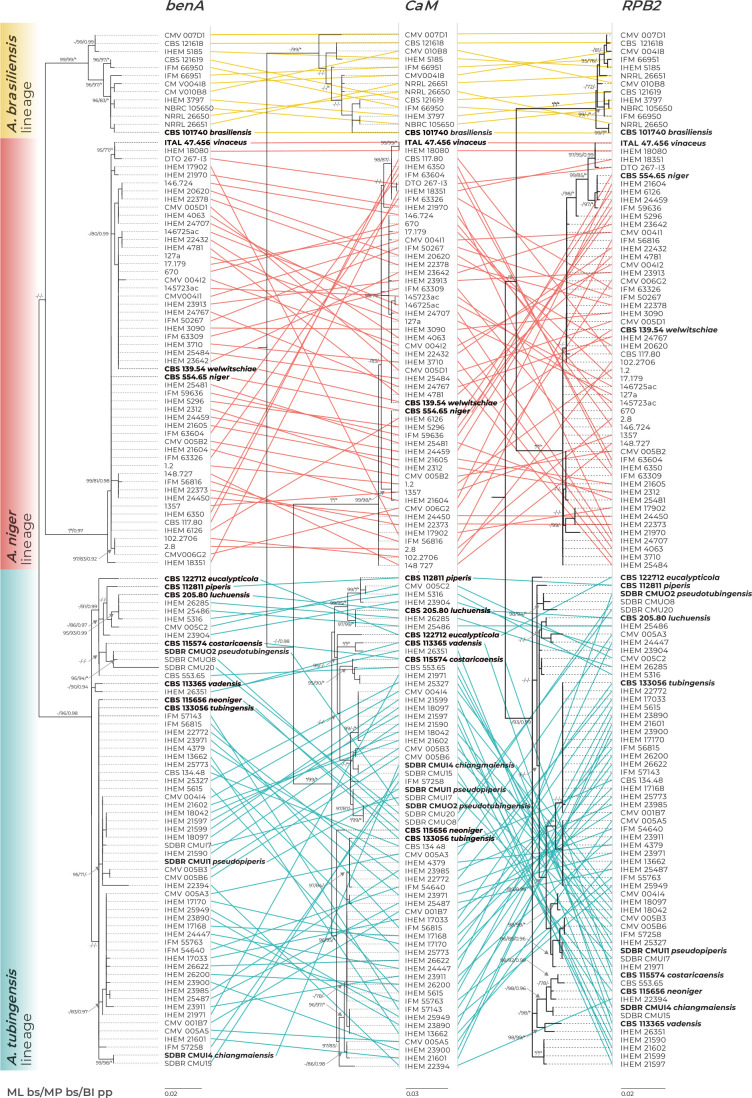
Fig. 2.
Comparison of single-gene genealogies based on the benA, CaM and RPB2 loci and created by three different phylogenetic methods (only one isolate per unique multilocus haplotype is included in each phylogeny). The coloured connecting lines show changes in the positions of isolates between single-gene trees (the branches were rotated so that the trees maximally correspond to each other). Best-scoring single-locus maximum likelihood (ML) trees are shown; ML ultrafast bootstrap support values (ML bs), maximum parsimony bootstrap support values (MP bs) and Bayesian inference posterior probabilities (BI pp) are appended to nodes. Only support values ≥95 %, ≥70 % and ≥0.95, respectively, are shown. A dash indicates lower statistical support for a specific node, or the absence of a node in the phylogeny, while an asterisk indicates full support. The ex-type strains are designated with a bold print. Alignment characteristics, partitioning schemes and substitution models are listed in Supplementary Table S1.