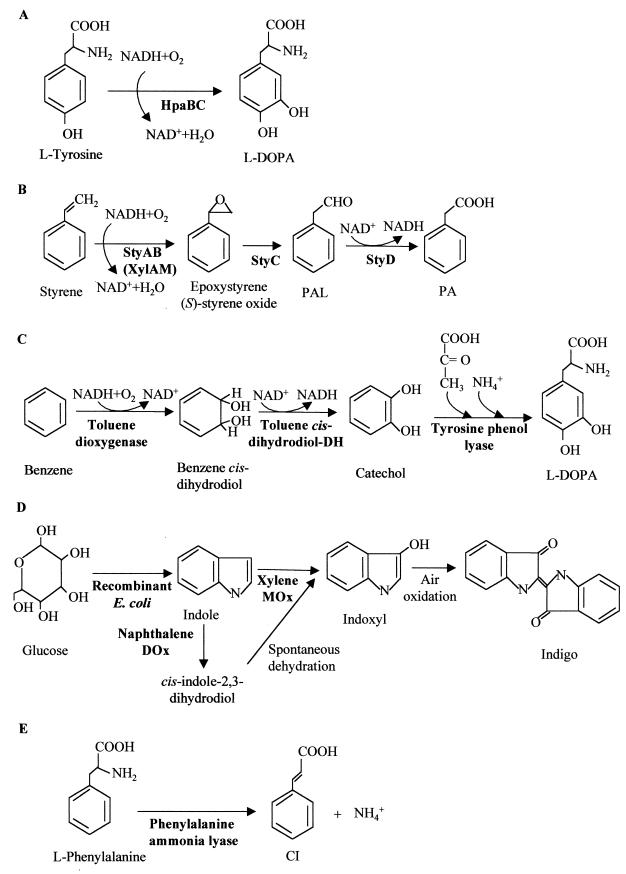
FIG. 12.
Selected biotransformations of aromatic compounds in recombinant E. coli strains. The enzymes catalyzing the different reactions are indicated in boldface type. (A) Production of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-Dopa) from tyrosine through the 4HPA monooxygenase (HpaBC) from E. coli W. (B) Biotransformation of styrene into (S)-styrene oxide (epoxystyrene), phenylacetaldehyde (PAL), and PA by the StyAB, StyC, and StyD enzymes from different Pseudomonas strains. Formation of (S)-styrene oxide from styrene was also reported using the xylene monooxygenase (XylAM) from the TOL plasmid of P. putida. (C) Conversion of benzene into l-Dopa using the toluene dioxygenase and toluene cis-dihydrodiol dehydrogenase (DH) from P. putida F1 and the tyrosine phenol-lyase from C. freundii. (D) Biotransformation of glucose into the dye indigo in a recombinant E. coli strain that converts glucose into indole and then oxidizes the latter through naphthalene dioxygenase (DOx) or xylene monooxygenase (MOx) from P. putida. (E) Conversion of l-phenylalanine to cinnamic acid (CI) and ammonia through the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase of R. toruloides.