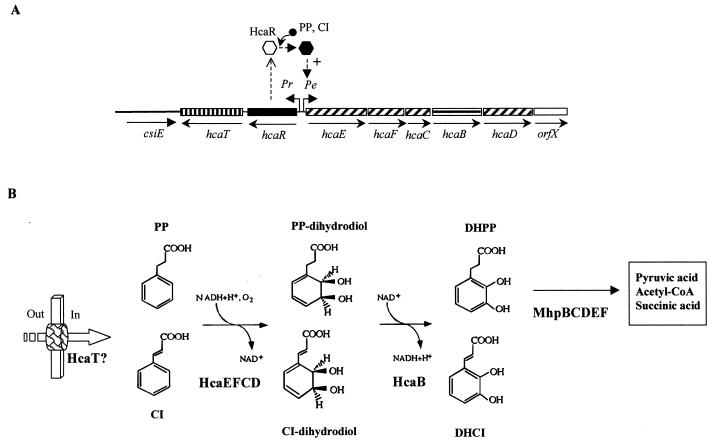
FIG. 4.
Pathway for the catabolism of PP in E. coli. (A) Genetic map of the chromosomal hca cluster. Relevant genes are indicated by blocks: genes with similar shading encode the subunits of the PP dioxygenase. Regulatory (solid block) and putative transport (vertically striped block) genes are also shown. The horizontally striped block indicates the gene encoding the PP dihydrodiol dehydrogenase. The empty block represents a gene of unknown function. The csiE gene flanking the hca cluster is represented by a thick line. The arrows show the directions of gene transcription. Bent arrows represent the Pr and Pe promoters. The inactive and active forms of the HcaR activator are represented by empty and solid hexagons, respectively. + indicates transcriptional activation. The inducer molecule (PP and CI) is represented by a solid circle. (B) Biochemistry of the PP catabolic pathway. The metabolites are PP, CI, PP dihydrodiol, CI-dihydrodiol, DHPP, and DHCI (see the legends to Fig. 2 and 3). The enzymes are HcaEFCD (PP dioxygenase), HcaB (PP-dihydrodiol dehydrogenase), and MhpBCDEF (see the legend to Fig. 2). The putative PP/CI transport protein (HcaT) is represented by a thick arrow. Out and In indicate outside and inside the cell, respectively.