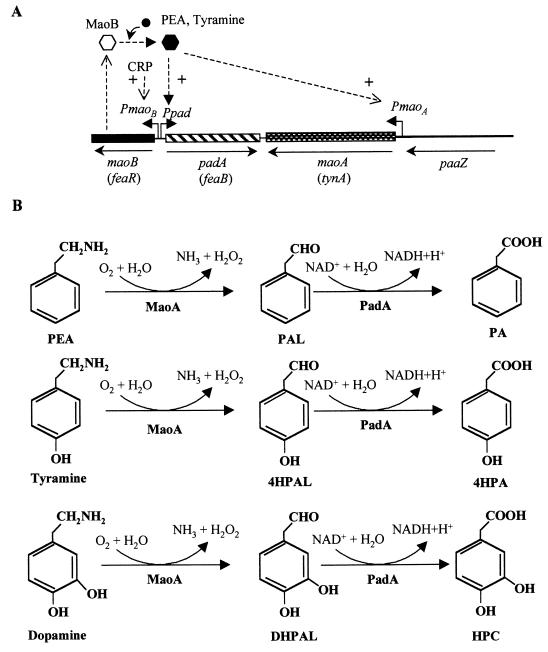
FIG. 6.
Upper pathway for the catabolism of aromatic amines (PEA, tyramine, and dopamine) in E. coli. (A) Genetic map of the chromosomal cluster for the initial catabolism of aromatic amines. Relevant genes are indicated by blocks. Alternative gene names are in parentheses. The paaZ gene from the paa cluster (see Fig. 5) is indicated by a thick line. The arrows show the directions of gene transcription. Bent arrows represent the PmaoB PmaoA and Ppad promoters. The regulatory gene maoB (feaR) is shown by a solid block. The inactive and active forms of the MaoB activator are represented by empty and solid hexagons, respectively. + indicates transcriptional activation. The inducer molecule (PEA, tyramine) is represented by a solid circle. (B) Biochemistry of the initial catabolism of aromatic amines. The metabolites are PAL (phenylacetaldehyde), 4HPAL (4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde), DHPAL (3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde), PA, 4HPA, and HPC (homoprotocatechuate). The enzymes are MaoA (monoamine oxidase) and PadA (phenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase).