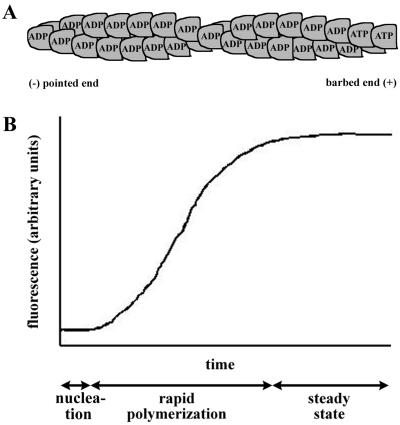
FIG. 2.
Actin filament structure and assembly dynamics. (A) Asymmetric homopolymer of helically arranged actin. The pointed or minus end (left) and barbed or plus end (right) are indicated. ATP bound to the actin monomer is hydrolyzed to ADP shortly after addition to the filament. (B) Actin polymerization curve. An idealized curve from a pyrene actin assay is shown. Actin is polymerized in vitro under experimental test conditions. At time zero, potassium and magnesium are added. The lag phase represents the time required for actin nucleation. The rapid polymerization phase represents the time during which short filaments elongate. Steady state represents an equilibrium between growth of the filaments due to monomer addition and shortening of the filaments due to loss of monomer.