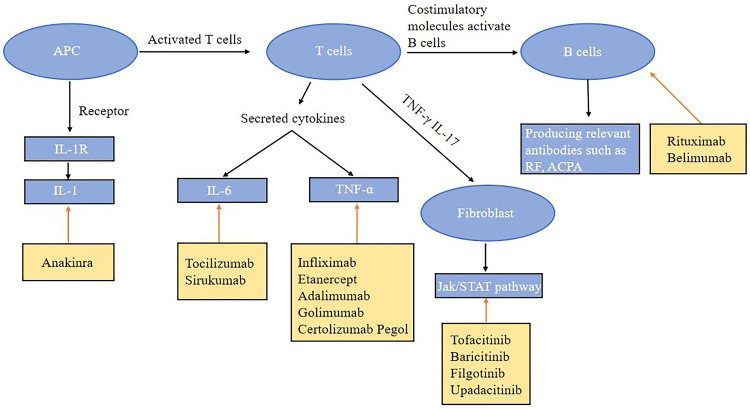
Figure 1.
Biological and targeted agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Antigen-presenting cells deliver their own antigens via major histocompatibility complexes to T cells, releasing lymphokines and activating macrophages to provide assistance to B cells. The latter may be induced to produce autoantibodies such as anti-citrullinated proteins. Autoantibodies are bound to the respective autoantigens and form immune complexes in the synovial membrane. These immune complexes bind to macrophages and other cells via Fc receptors and complement receptors, activating the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other inflammatory mediators like tumor necrosis factor, interleukins and macrophages via lymphokines, such as T-cell interferon or IL-17.